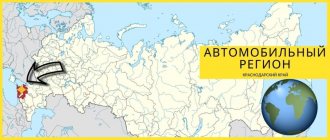
The code 23 of the Russian region is assigned to the Krasnodar Territory, geographically located in the southwest of the Russian Federation . The territorial entity has land borders and access to the sea. In terms of the number of residents at the beginning of 2020, the territory occupied 3rd position among other regions of the Russian Federation .
Main city
The capital is Krasnodar (called Ekaterinodar until 1920), built on the right bank of the Kuban River. The city is located at a distance of 120 km from the Black Sea coast, the distance from Moscow is 1300 km (by road, in a straight line - 1192 km). The number of residents, including suburbs, at the beginning of 2022 is more than 1022 thousand.
The city was founded as a fortified area at the end of the 18th century and received its original name in honor of Empress Catherine II, who donated land for the construction of the first fortress.
[edit] Population
The population of the region is 5,106.3 thousand people, of which 2,372.8 thousand people are men, 2,733.5 thousand people are women. The share of the urban population is 53.4%. The share of the rural population is 46.5%. The economically active population is 3,072.4 thousand people. The number of people employed in the economy is 2,103.3 thousand people. The unemployment rate according to the ILO methodology is 10.1%. The number of people over working age is 26.3%, under working age - 13.4%. The natural increase rate is negative, amounting to −5.4 per 1,000 population. The migration growth rate is positive, amounting to 34.0 per 10,000 population.
Vehicle code
Civilian and military vehicles undergoing initial registration since the mid-90s. last century, received signs with code 23 (which region is encrypted with the code can be found out in reference books that are freely available). The plates have standard sizes; starting from 2022, it is possible to produce license plates according to the American or Japanese standard (in accordance with the landing area on the rear of the body).
The license plate allows you to determine whether it is the 23rd or 123rd region, but it is impossible to find out which city it is. The plates are sent to regional MREO traffic police departments in a random sequence in packs of 100 pieces; reference to a populated area is not provided. On some cars in the Krasnodar Territory , region 93 is registered; the driver can find out in which region of Russia the registration actions were carried out. But where the car came from by the number; information must be requested through official channels in the traffic police.
[edit] Notes
- [1]
- [2]
- [3]
- [4]
- [5]
- Krasnodar. Retail real estate. November 2020
- Krasnodar. Retail real estate. November 2020
- Krasnodar. Retail real estate. November 2020
- [6]
| Subjects of the Russian Federation | |
| Central Federal District | Belgorod region • Bryansk region • Vladimir region • Voronezh region • Ivanovo region • Kaluga region • Kostroma region • Kursk region • Lipetsk region • Moscow region • Oryol region • Ryazan region • Smolensk region • Tambov region • Tver region • Tula region • Yaroslavl region • Moscow |
| Northwestern Federal District | Karelia • Komi • Arkhangelsk region • Nenets Autonomous Okrug • Vologda region • Kaliningrad region • Leningrad region • Murmansk region • Novgorod region • Pskov region • St. Petersburg |
| Southern Federal District | Adygea • Kalmykia • Crimea • Krasnodar region • Astrakhan region • Volgograd region • Rostov region • Sevastopol |
| North Caucasian Federal District | Dagestan • Ingushetia • Kabardino-Balkaria • Karachay-Cherkessia • North Ossetia • Chechnya • Stavropol Territory |
| Volga Federal District | Bashkortostan • Mari El • Mordovia • Tatarstan • Udmurtia • Chuvashia • Perm region • Kirov region • Nizhny Novgorod region • Orenburg region • Penza region • Samara region • Saratov region • Ulyanovsk region |
| Ural Federal District | Kurgan region • Sverdlovsk region • Tyumen region • Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug • Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug • Chelyabinsk region |
| Siberian Federal District | Altai • Tyva • Khakassia • Altai Territory • Krasnoyarsk Territory • Irkutsk Region • Kemerovo Region • Novosibirsk Region • Omsk Region • Tomsk Region |
| Far Eastern Federal District | Buryatia • Yakutia • Trans-Baikal Territory • Kamchatka Territory • Primorsky Territory • Khabarovsk Territory • Amur Region • Magadan Region • Sakhalin Region • Jewish Autonomous Region • Chukotka Autonomous Okrug |
Source - ""
Category: Krasnodar region
Coat of arms of the region
The coat of arms contains a green central shield with an image of a fortress, behind is a golden shield with a black imperial eagle. On top of the shields is a stylized princely cap , and along the lower edge there is a double ribbon of the Order of Lenin (introduced in 2004). For the image on the flags, a simplified version of the coat of arms is used (golden color with black ornaments).
Flag of the region
Since the spring of 1995, a flag of 3 horizontal stripes of blue, crimson and green has been used as a flag ( where the outer stripes are 2 times narrower than the central one). In the center is a golden-colored coat of arms (depending on the date of manufacture of the flag, the coat of arms may have an old or new look). The color combination of the cloth corresponds to the symbolism of the Kuban Cossacks.
Nationalities
Conducted in 2002 and 2010. All-Russian population censuses made it possible to determine the national composition of the inhabitants of the territory; the data (in% of the total) are presented in the table . The reporting did not include citizens who refused to indicate their nationality or found it difficult to answer. Nationalities numbering less than 0.1% of the total population are not listed.
| Nationality | Data 2002, % | Data 2010, % |
| Russians | 86,3 | 88,2 |
| Ethnic Cossacks | 0,3 | 0,1 |
| Armenians | 5,4 | 5,5 |
| Ukrainians | 2,6 | 1,6 |
| Greeks | 0,5 | 0,4 |
| Belarusians | 0,5 | 0,3 |
| Tatars | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| Georgians | 0,5 | 0,3 |
| Ethnic Germans | 0,5 | 0,2 |
| Adyghe people | 0,4 | 0,3 |
| Turks | 0,3 | 0,2 |
| Azerbaijanis | 0,3 | 0,2 |
| Gypsies | 0,1 | 0,3 |
| Ossetians | 0,1 | 0,1 |
Content
- 1 Geography
- 2 Population
- 3 Economy 3.1 Industry 3.1.1 Electric power
- 3.1.2 Mechanical engineering
- 3.1.3 Forestry and wood processing industry
- 3.1.4 Fuel industry
- 3.1.5 Food industry
- 4.1 Video
Transport
The region has a developed transport network, represented by:
- airports capable of receiving large aircraft;
- highways of federal and local subordination;
- railways belonging to the North Caucasus branch of Russian Railways;
- seaports providing import and export of various goods and raw materials.
Air
The region, with its center in Krasnodar, is distinguished by a developed network of airports united under the auspices of the BAZEL Aero group. Airfields in Krasnodar (among the top 10 largest in Russia in terms of passenger flow), in the cities of Anapa and Sochi are classified as international, and there are local airfields in Gelendzhik and Yeisk.
Automotive
The following roads pass through the territory :
- federal highway M4 , connecting the capital of the Russian Federation with the cities of Krasnodar and Novorossiysk;
- highways P217 , A290 and 147 , allowing car to travel both within the region and to get to cities in neighboring regions;
- local highways A146 , A148 and P253 .
Railway
Railway tracks on the territory of the entity with region code 23 are the property of Russian Railways. There are transit routes that allow you to transport goods and people to neighboring territories and regions , as well as to the Republic of Crimea. There is a narrow-gauge Absheronskaya road, used for the delivery of goods and of interest to tourists.
Water
Krasnodar Territory with region number 23 , which has access to the Black and Azov Seas, has a developed water transport network. The port cities of Yeisk, Taman, Anapa, Novorossiysk and a number of others are located in the coastal zone. Ports account for about 40% of Russian freight transport by sea and river routes. The region is a major transshipment point on the route of Russian oil exports.
Characteristics of the Krasnodar region
Kuban is the name given to the territory of the Krasnodar Territory, one of 89 objects of the Russian Federation, occupying an area of only 0.44% of the all-Russian one - 78 thousand square meters. km, but having much greater weight due to its geographical location, proximity to the two southernmost seas - the Black and Azov, developed sanitary-resort and tourist infrastructure, transport network, and the presence of favorable natural conditions.
The Krasnodar region has significant natural resource potential, international airports, and a developed network of roads and railways. Having direct access to international sea routes, the Krasnodar Territory realizes Russia’s interests in the Black Sea and Mediterranean economic cooperation zones.
The Krasnodar Territory borders in the north and northeast with the Rostov region, in the east and southeast - with the Stavropol Territory and the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, in the south - with Georgia. From the west, southwest and south, the region is washed by the waters of the Azov and Black Seas. The length of the borders is 14,540 km, including 800 km by land and 740 km by sea. The northernmost point is 372 km from the southernmost point, and the westernmost point is 380 km from the easternmost point.
The Krasnodar Territory is a region of Russia and is located approximately midway between the equator and the pole, at the latitude of Northern Italy and Southern France. The Kuban Plain lies on the ancient Scythian plate with a thickness of about two kilometers. The climate in the flat part of the region is moderately warm, with hot summers and mild winters; on the Black Sea coast - transitional to subtropical (from Anapa to Tuapse) and subtropical (from Tuapse to Adler). The average January temperature is from +4, +5° C, in the Anapa region to −8° C in the mountains at an altitude of 2000 m, the July temperature is +22, +24° C on the plain and +12, +13° C in the mountains . Summer lasts 4-5 months, autumn and winter are warm.
The soil of the region is represented by rich, fertile chernozems in the northern steppe right bank, southern left bank mountain strips, as well as along the entire lower reaches of the Kuban River and in the foothills. Kuban chernozems, reaching a humus layer thickness of over 120 cm, are one of the main riches of the region and Russia.
The river system of the Krasnodar Territory consists of the Azov-Kuban lowland, the Kuban River and its tributaries, as well as the Black Sea basin. It has more than 13 thousand rivers, rivers and streams. The Kuban River, the main water artery of the Krasnodar Territory, has a length of 870 km and divides the region into the northern steppe right bank and southern elevated left bank parts. The rivers of the Black Sea region have large slopes and often look like mountain streams.
Lakes have always attracted people with their unique beauty, clean air, and the peace and tranquility that reigns on their shores. There are lakes in the Krasnodar Territory both along the shores of Azov and the Black Sea (Khanskoye, Golubitskoye, Solenoye, Chemburka), and in the valleys of steppe rivers. Mountain lakes stand out especially. The largest freshwater lake in the Krasnodar Territory is Lake Abrau, located at an altitude of 84 km, its area is 1.6 square meters. km. The champion of beauty is the high-mountain lake Kardyvach, surrounded by rocky bastions of 3-kilometer peaks. There are many unknowns hidden in the dwarf lakes - Khyzhi (sacred among the Circassians, Tuapse district), Verkhneafipsky Loch Nessie (Seversky district), Mertvoe (Goryacheklyuchevsky district) and many others.
The largest Azov-Kuban basin of fresh groundwater in Europe is located on the territory of the region. More than 60 types of minerals have been discovered in the depths of the Kuban, which occur mainly in the foothills and mountain regions. The Krasnodar region is rich in deposits of marble, limestone, marl, sandstone, gravel, quartz sand, as well as reserves of oil, natural gas, iodine-bromine and healing mineral waters.
More than 200 mineral springs of medicinal value have been discovered in various areas of the region. Warm seas and a healing climate, unique natural mineral springs and healing mud have earned Kuban the reputation of one of the most popular resort and tourist regions of the country.
Matsesta springs are world famous for curing diseases of the joints, respiratory organs, skin and nervous disorders. Goryacheklyuchevsky hydrogen sulfide waters are effective for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and rheumatism. In Yeysk, joint diseases and radiculitis are treated. Zaporozhye springs are similar in composition to the waters of Essentuki. The Semigorsk springs, near Anapa, enjoy well-deserved fame.
The forest is of great environmental importance and is the main source of valuable timber. The total forest area of the Krasnodar Territory is over 18 million hectares. Oak and beech tracts of industrial importance occupy 68% of the area of all forests, where hornbeam, chestnut, fir, spruce, and fruit trees - pear, apple, and cherry plum - are also represented.
The zone from Tuapse to Adler along the Black Sea coast is subtropical. Citrus fruits grow here - tangerines, oranges; tea plantations spread out.
There are 64 glaciers in the mountainous areas of the Krasnodar Territory. Almost all of them are located on the Main Caucasus Range and its northern spurs. On the slopes of the Pseashkho massif there is the largest glacier, Kholodny, and the westernmost glacier in the entire Caucasus is hidden on the slopes of Mount Fisht.
The fauna of Kuban is rich and diverse. In total there are 86 species of mammals, 3200 of birds, 163 of fish, 21 of reptiles, 11 of amphibians. Among them there are many listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation and Kuban. A significant area is occupied by protected areas and national parks. If the forests are predominantly inhabited by deer, bears, chamois, aurochs, wild boars and other mammals, then in the Azov floodplains there is a kingdom of birds - pelicans, herons, ducks, swans.
No region of Russia can compare with Kuban in terms of development of viticulture and winemaking. 51 farms here grow grapes, and 34 process grapes and produce wine products known outside the region and Russia.
The Krasnodar Territory was formed on September 13, 1937 and is part of the Southern Federal District of the Russian Federation. The administrative center of the Krasnodar Territory is the city of Krasnodar. The distance from Krasnodar to Moscow is 1539 km.
The region has 38 districts, 15 cities of regional subordination, 11 cities of regional subordination, 11 intra-city districts and districts, 21 urban-type settlements, 390 rural administrations, 1,719 rural settlements. The largest cities of Kuban are Krasnodar, Sochi, Novorossiysk, Armavir, Yeisk, Gelendzhik, Kropotkin. Krasnodar is the administrative, economic and cultural center of the region.
Krasnodar Territory is the third largest subject of the Russian Federation: 3.5% of the Russian population lives here. The population density is 66 people per square meter and is 8 times higher than the Russian average.
The region is home to 5 million 124 thousand people, including 2 million 739 thousand in cities and towns and 2 million 384 thousand people in rural areas. Residents of the regional center number more than 790 thousand people, or 15% of the region's population. The population of the region is represented by more than 100 nationalities. The main part are Russians (86.1%).
Armenians make up 4.9% of the total population of Kuban, Ukrainians - 3.9%, Belarusians - 0.7%, Adygeis - 0.6%, Greeks - 0.4%, other nationalities - 3.4%.
In recent years, the population of the Krasnodar Territory, as well as in Russia as a whole, has been declining. However, the share of the working-age population has increased over the past three years from 56% to 57.5%.
The region's labor resources on an annual average are about 3 million people (or almost 60% of the total population), the total number of people employed in the economy is more than 2 million people. In recent years, the situation on the labor market has been stable. It is characterized by:
- growth in the number of people engaged in economic activity, mainly due to
- increasing employment in the private sector;
- a steady decline in total and registered unemployment.
Over 14 thousand people were employed after completing vocational training organized by employment services. In total, almost 22 thousand people completed such training in specialties that are in demand in the labor market, and 172 thousand people received career guidance services.
Particular attention is paid to the employment of socially weakly protected citizens. In accordance with the regional law, there are quotas for jobs for people who are especially in need of social protection and have difficulty finding work.
Krasnodar region is one of the most significant economic regions in the Russian Federation. In terms of socio-economic development, Kuban ranks in the top twenty among 89 regions of the country, and in the top ten in terms of gross regional product.
The socio-economic development of the region in recent years has been largely determined by all-Russian trends that emerged after the 1998 crisis, and by tax, budget, social policies, and institutional reforms carried out at the federal level.
In recent years, the economy of Kuban has reached a sustainable pace of development. Since 1997, the rate of decline in many sectors of the Kuban economic complex has slowed. During 1999-2003, the progressive development and growth of business activity in the real sector of the economy was ensured. The own revenues of the consolidated budget of the Krasnodar Territory are growing dynamically; in 2002, the increase amounted to almost 8 billion rubles. According to a comprehensive assessment of the socio-economic development of Russian regions, conducted by the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation, the region’s rating has risen by 16 places, while many development indicators exceed all-Russian parameters.
The share of the region's GRP production in the all-Russian gross domestic product has stabilized at 2.1%. The positive dynamics of growth of the region's GRP is ensured by increasing the volume of production of products and services in the main sectors of the economy in the amount of 1.4-1.8 times. The largest share in the structure of the region's GRP comes from agriculture.
The basis of the region's economic potential is transport, agricultural, fuel and energy, resort and recreational complexes, food industry, mechanical engineering, forestry, woodworking and furniture production, and the building materials industry. Positive dynamics of development of most of the main sectors of the region's economy also took place in 2003.
The region is traditionally attractive for banking structures. In terms of their level of representation, it is second only to Moscow and St. Petersburg. Over the past years, the economy of the Krasnodar region has become increasingly open. The liberalization of foreign trade in the early 90s contributed to the active development of trade relations between the region and foreign countries. The Krasnodar region occupies a leading place in the foreign economic activity of the South of Russia.
The high level of prices on the world market for oil and petroleum products ensured significant growth rates in regional exports, and the reduction in domestic market demand for imported food products resulted in a decrease in the volume of purchases of food and agricultural raw materials.
The foreign trade turnover of the Krasnodar Territory is increasing year by year. The commodity structure of regional exports is dominated by oil and petroleum products (more than 70%). Exports also include grain crops and oilseeds, timber and woodworking products, mineral fertilizers, lathes and metal-cutting machines, and more.
The dynamics of the total volume of imports of goods is characterized by minor fluctuations, but its structure has changed significantly in recent years. There has been a steady trend of growth in purchases of industrial products (machinery and equipment, transmission devices, ferrous metals) with a simultaneous decrease in the share of imports of food products. The leading partners of the region are the following countries: USA, Germany, Italy, Turkey, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Republic of Belarus. The geography of foreign trade in recent years has been characterized by an increase in the share of trade with non-CIS countries.
Foreign trade turnover of services is growing rapidly. The structure of exports of services is dominated by transport services, imports of services - construction, business services - mainly consulting services on management issues and services in the field of research and development.
Stabilization and the emerging economic recovery in recent years have led to a noticeable increase in the standard of living of the population. The positive dynamics of real cash incomes of the population and real wages are being restored.
Regional legislation is being improved. Legislative and regulatory acts of the Krasnodar Territory have been adopted, making it possible to intensify the processes of socio-economic stabilization. The structure and mechanism of management in various industries is being improved. Small business has become a more visible and significant sector of the economy: in terms of the volume of products produced and the number of operating enterprises, it holds first and second places, respectively, in the Southern Federal District. Such approaches are the basis for sustainable economic growth in the coming years.
At the beginning ↑ “Main” Behind ← “Governor of Kuban” Ahead → “The emergence and development of cooperation in Kuban”
Sights of Krasnodar
On the territory of the city of Krasnodar, 23rd district, there are several large churches (for example, St. Catherine's Cathedral). There is one of the surviving water towers in Russia according to the design of engineer V.G. Shukhova. A large number of monuments have been erected (more than a hundred), some of which were installed after 2010 (for example, to the district police officer Aniskin); on the territory of Krasnodar there are numerous fountains with lighting and music.
Climate
There are several climatic zones in the region.
- The area from Anapa to Tuapse is in the Mediterranean climate zone.
- Sochi and its surroundings are classified as subtropical.
- The rest of the Kuban territory is in the temperate continental climate zone.
The coastal area from Anapa to Gelendzhik differs from other parts of the region in strong winds. They are most sensitive in Novorossiysk from November to March. Wind speed can reach 47 m/s.
Average air temperature in January:
- on the plain -3-5°C;
- on the coast from 0 to +6°С;
- in Sochi +5-9°С.
In summer, the thermometer can rise above +45-47°C.