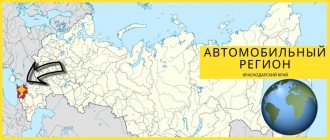
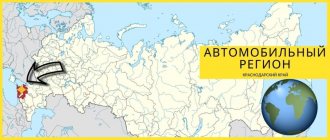
Location of the Krasnoyarsk Territory on the map of Russia
The Krasnoyarsk Territory on the map of Russia is located within Central Siberia. Its territory is surrounded by 2 seas: the Laptev and Kara. On the south side are the Sayan Mountains. The size of the region is 1250 km. It includes Taimyr (the largest Russian peninsula).
Its area is adjacent to:
- 2 independent administrative-territorial units: Evenki and Taimyr districts, which exceed the territory of Germany by 6 times;
- 41 urban-type settlements;
- cities (24 pcs.);
- districts, the number of which reaches 42 units.
The region belongs to the central part of Asian Russia. The northernmost point of Asia and the Russian Federation is Cape Chelyuskin.
History of education
And it all started quite ordinary for most Russian cities, formed during the development of Siberian lands in the 16th-18th centuries. It was a wooden fort founded on the Yenisei, at the confluence of the Kachi River. In 1628, from the moment the Cossacks under the leadership of the nobleman A. Dubensky founded a wooden fortress, the history of one of the largest cities in the Siberian Federal District - Krasnoyarsk - began. What was the history of this wonderful city, one of the ancient and beautiful cities of Siberia? It is full of significant events related to the history of Russia.
The fortress had five observation towers, which were connected by walls. It was surrounded by a rampart and a ditch filled with water. Not far away, on the Kum-Tigey hill (the modern name is Karaulnaya Mountain), an observation tower was erected to monitor the area. If the enemy approached, the guards lit a fire, which warned of the enemy, preventing the Cossacks from being taken by surprise.
The gates of the fort were closed, and he was preparing to repel the raid of the Turkic and Mongol tribes. The fort served as protection for the cities of Yeniseisk and Tomsk, and over time, the villages of settlers located in the district and located in the zone protected by the Cossacks.
Short story
Approximately 200 thousand years ago, the first people settled on the territory of the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
Before the advent of the Russian nation, this area was inhabited by the following tribes:
- Yenisei;
- Samoyed;
- Turkic;
- Tunguska
The Yenisei fort was created in 1619. It occupies a significant place in the settlement of Siberia by the Russian population.
The Krasnoyarsk Territory was an integral part of a large territory, the capital of which was in Tobolsk until the end of the 20s. 17th century. The Yenisei fort became a city in 1676. It included all the settlements along the Yenisei, as well as the right bank lands that stretched to Transbaikalia.
At the beginning of the 18th century, Peter 1 endowed the province with broad powers. It consisted of provincial settlements.
Managing the lands of the Siberian province was accompanied by certain difficulties, since there were too large distances between settlements, and the transport system was poorly developed. There was a question about introducing territorial reform. Over time, 5 provinces and 7 counties joined the province.
The Yenisei province was created in the 20s. 19th century. Krasnoyarsk was chosen as its capital. The province was considered the largest gold mining region in Russia. This prompted the productive development of agriculture and the development of activities related to the movement of ships along waterways.
The Krasnoyarsk region appeared on the map of Russia in 1934. During the Second World War, its industry actively developed. By the beginning of the 90s. There is growth in the areas of culture, education, industry, and science in the region. In the 21st century, this area has a well-developed economic system and culture.
Krasnoyarsk (Russia): general information about the city
This is one of the largest cities in the Asian part of the country, an important industrial, cultural and educational center of Siberia. Today, about one and a half million people live in the Krasnoyarsk agglomeration. Thus, it is the easternmost millionaire city in Russia. The total area of Krasnoyarsk is 354 square kilometers.
Krasnoyarsk was founded back in 1628 as a fort, the purpose of which was to protect Russian lands from raids by nomads. The city's name comes from the brownish color of the local rocks, which are of volcanic origin.
Modern Krasnoyarsk is called the economic capital of all Eastern Siberia. The metallurgical, chemical, woodworking and space industries are quite developed here. Hydropower and mechanical engineering enterprises operate in the city. Krasnoyarsk, among other things, is the most important educational center in Siberia. In total, over 150 thousand students live and study in the city.
Climate, weather by month
The region is dominated by sharply continental and temperate continental climates. The temperature changes every season. The climate is heterogeneous because it is located at a considerable distance from the center of the globe. There are several climatic zones here. These include: temperate, subarctic and arctic.
The most comfortable time to relax is summer. Temperatures range from +20.8°C to +26.4°C. It rains rarely, about once a month. The number of sunny days in June, July, and August reaches 20 days. Autumn begins in August. This time is characterized by fierce winds and snowfalls. Since September, winter has reigned here. There are no thaws. In some regions, daytime temperatures reach -40°C.
Spring comes here by mid-May. The air temperature during the day becomes +5°C. In spring there is little sun and quite cold, and precipitation may occur in the form of snow.
Each month has its own temperature, which has average values in this table:
| Name of the month | Daytime temperature | Night temperature |
| January | -16°С | -19°С |
| February | -14°C | -18°С |
| March | -2°C | -10°С |
| April | +9°С | +2°С |
| May | +13°С | +4°С |
| June | +23°С | +8°С |
| July | +26°С | +13°С |
| August | +20°С | +8°С |
| September | +15°С | +3°С |
| October | +2.5°С | -5°C |
| November | -12°С | -15°С |
| December | -12°С | -15°С |
Timezone
- The time difference between the Krasnoyarsk Territory and Moscow is +4 hours.
- Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) +7 hours.
- Sunrise occurs at 09:00. 19 min.
- Sunset at 16:00. 16 min.
- Daylight hours usually last 06 hours. 57 min.
Lakes
The Krasnoyarsk Territory (its borders are clearly visible on the map of Russia) has 323 thousand lakes. The area of their water surface exceeds 10 hectares. Due to the rapid melting of snow, many new lakes appear every few years.
Approximately 86% of the total number of lakes in the Krasnoyarsk Territory are located outside the Arctic Circle. The largest is considered Taimyr with a length of the upper layer of 4560 km2. Large Krasnoyarsk lakes also include Pyasino, Lama, Bolshoye Khantaiskoye and Keta.
Up to 16 thousand lakes are located only in the center of the region. On its southern side there are over 4 thousand. Water from individual lakes is used to treat various diseases.
List of counties
FOs were created by decree of President Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin in the spring of 2000. At that moment, 7 such territorial-administrative units were formed. In 2010, President Dmitry Anatolyevich Medvedev, by decree, removed the Southern Federal District from the structure and created a new unit - the North Caucasus Federal District. In 2014, the ninth, Krymsky, appeared, but in 2016 it was transferred to the Southern Federal District. Since then, no quantitative changes have been made.
Central
The Central Federal District is the only one that does not include republics. It contains only regions and one city of federal significance - Moscow, which is the center. It has the highest population density (60.37 people per square kilometer) and the highest population - almost 40 million people. More than 80% of all citizens live in cities. Most of them are registered in Moscow and the Moscow region.
Northwestern
It consists of 11 subjects, the number of residents is almost 14 million. Most of the territories are located in the European part of the north. The climate is greatly influenced by the Arctic and Atlantic seas, as well as a large number of different bodies of water. Thanks to its many forests, it is of great tourist and economic importance. Many minerals are mined here, as well as oil.
Southern
Based on the name, it is clear that it is located in the south of the European part. Number of inhabitants: 16.5 million. 62% of all people live in cities. From May 13 to June 21, 2000, it had a different name - North Caucasian Federal District. Consists of 8 subjects.
North Caucasian
Consists of 7 administrative-territorial units of the Russian Federation, the population does not exceed 10 million. The smallest in terms of footprint. It borders with a number of neighboring states - Abkhazia, Azerbaijan and Georgia. All borders are land, but there is one water border - with the Republic of Kazakhstan. A special feature is the national composition - less than a third of all citizens are Slavs.
Privolzhsky
It consists of 14 subjects and has no access to the World Ocean. Almost a fifth of the population of the entire country lives in the Volga Federal District - almost 30,000,000 people, almost three-quarters of whom live in cities. The concepts of the Volga Federal District and the Volga region should not be confused; these are completely different geographical units.
Ural
There are no republics, only regions and autonomous okrugs (among the latter are Yamalo-Nenets and Khanty-Mansiysk). The most useful in terms of filling the budget are the latter; they form over 30% of all incoming financial resources. It has an external border with the Republic of Kazakhstan. The largest number of citizens live in the central and southern parts, since large settlements are located there.
Almost every administrative-territorial unit contains large mineral deposits. Oil and gas are also actively extracted in the Ural Federal District. Due to this, large revenues to the budget are ensured. A large number of agricultural lands are actively used in the agricultural sector.
Siberian
It consists of 10 administrative-territorial units, including republics, regions and territories. It occupies a quarter of the entire area of the country. 2022 was marked by the transfer of Buryatia, Trans-Baikal Territory, to the Far Eastern Federal District. The population is about 17,000,000 citizens.
Far Eastern
The Far Eastern Federal District is located in the Far East (as reflected in the name), as well as part of Eastern Siberia. It occupies about 40% of the state's area and is the largest. Almost all administrative-territorial units have access to large bodies of water. It neighbors five countries - China, North Korea and Mongolia on land, as well as the United States of America and Japan on water. A special feature is the absence of million-plus cities.
Rivers
The rivers of the Krasnoyarsk Territory are its main asset. They originate in the south and flow to the north of the region. Belongs to the waters of the Arctic Ocean. The Yenisei is considered the most abundant river. Its surface performs a warming function for the Arctic Ocean. The length of the river is 3487 km.
The following flows through the territory of the region:
- 35,024 rivers that are considered small (up to 10 km);
- 15 rivers – more than 500 km;
- 160 pcs. length from 100 to 500 km.
The total length of all rivers is 175 thousand km. These measurements are approximate because some rivers dry up while others appear regularly.
The rivers flowing in the northern side of the Krasnoyarsk territory are smaller than the Yenisei. But they are also rich in water. For example, the Khatanga River is about 2 km wide, and at some points reaches 6 km.
The Lower and Podkamennaya Tunguskas are filled with a lot of water in the spring season. The confluence of this river into the Yenisei is a magical phenomenon that is recommended to be observed in the summer. At this time there is almost no night, the sky turns pink, beautifully reflected in the water.
The Krasnoyarsk Territory typically has 14 largest rivers with powerful hydropower potential:
- Yenisei – 3487 km;
- Khatanga – 227 km;
- Caen – 629 km;
- Angara – 1799 km;
- Sym – 699 km;
- Syda – 207 km;
- Pyasina – 818 km;
- Kureika – 888 km;
- Podkamennaya Tunguska – 1865 km;
- Lower Tunguska – 2989 km;
- Big Pit – 415 km;
- Tuba – 119 km;
- Oya – 254 km;
- Manna – 475 km.
Vegetation
Within the Krasnoyarsk Territory there is tundra. There are many dwarf shrubs, moss and lichens here. Poppies, cabbage, cereals, and cloves are grown. After the tundra begins the forest-tundra. On its territory there are unique deciduous trees. The taiga stretches almost along the entire edge. Vegetation here includes fir, larch, spruce, Siberian cedars, and taiga pine.
In the south of the Krasnoyarsk Territory there are black earth forest-steppes, which are plowed by people for working in the fields. In the southern part there is Mount Sayan. There is amazing nature here, practically untouched by people and having its original appearance. Vegetation such as feathery feather grass, slippers, May palmate root, and orchis are listed in the Guinness Book of Records.
Animal world
The fauna of the Krasnoyarsk Territory is distinguished by a wide variety of animals. Sheep live in the mountains. Here you can also meet a snow leopard. Reindeer are among the permanent inhabitants of the northern part of the region.
Pallas's cat lives in the Krasnoyarsk Territory and is listed in the Red Book
On the territory of the steppes it was noticed:
- gophers;
- hares;
- wolves;
- shrew;
- lynxes;
- wolverine.
The taiga part of the territory boasts the presence of squirrels, arctic foxes, ermines, sables, and foxes. Stolby is home to white hares, moose, martens, deer, musk deer, and brown bears. More than 400 species of birds exist in this side of Siberia (geese, storks, cranes, flamingos, petrels, swifts). In small numbers you can see newts, Siberian salamanders, and toads.
More than 50 species of fish live here. The most popular are catfish, pike, cod, salmon, smelt, carp.
The poor environmental situation indicates that a large number of animal species are included in the Guinness Book of Records. Many rare species of animals currently live exclusively in protected areas. These include herring whales, red wolves, Siberian roe deer, and fin whales. Siberian sturgeon and deer are at risk.
Interesting facts about Krasnoyarsk
Finally, we bring to your attention ten interesting facts about the city of Krasnoyarsk:
- in 1749, the first meteorite in Russia was found in the vicinity of the city;
- one of the largest waste processing plants in the country operates in Krasnoyarsk;
- the real “trick” of Krasnoyarsk is the fountains, of which there are 140 in the city;
- every summer, live palm trees from the local botanical garden are planted on the central streets of the city;
- on the 10-ruble banknote you can see several attractions of Krasnoyarsk, namely the local hydroelectric power station, the Communal Bridge over the Yenisei and the Chapel of Paraskeva Pyatnitsa;
- the first casino of the Soviet Union opened here, this happened in 1924;
- before the start of World War II, many Chinese lived in Krasnoyarsk;
- Krasnoyarsk resident Boris Smirnov was included in the Guinness Book of Records as the person who donated the largest amount of blood (68 liters);
- athletes from Krasnoyarsk became world champions in motorsports 21 times;
- sculptural compositions are another distinctive feature of Krasnoyarsk (the city is decorated with dozens of funny sculptures).
State of the environment
The environmental situation in the Krasnoyarsk Territory is not very high. There are hazardous industries operating in this area. They pollute the environment by throwing waste products into rivers and lakes. 0.7% of such enterprises operate in large populated areas, which include Norilsk and Krasnoyarsk.
An equally important problem is the destruction of forest areas by cutting them down. The local population does not take into account that forests not only have a beneficial effect on air purification, but are also home to many animals.
A minor role is given to flower plantings in populated areas. Due to these unfavorable factors, the Krasnoyarsk Territory is included in the Russian ranking of regions with poor environmental conditions.
To improve the environmental situation, it is recommended to create environmentally friendly enterprises that do not pose a threat to human life and health. It is important to devote a significant place in this issue to forest conservation, since it has a beneficial effect on the respiratory system and removes toxic substances from the environment.
Ecology and city improvement
The environmental situation in the city is far from ideal. The reason for this is numerous industrial enterprises, active mining of ferrous metals, as well as the burial of nuclear waste near the city. Air pollution is one of the primary environmental problems of modern Krasnoyarsk. It is felt most acutely by residents of areas located in lowlands. The atmosphere over Krasnoyarsk is polluted with carbon and nitrogen oxides, dioxides, formaldehydes and other substances.
The worst environmental polluters in the city are the following enterprises: Krasnoyarsk Aluminum JSC, Krasnoyarsk CHPP-1, CHPP-2, as well as a number of coal-fired boiler houses.
As for landscaping, everything is in perfect order in Krasnoyarsk. City streets are clean, well-groomed and very green. It is worth noting that Krasnoyarsk several times became “The Most Comfortable City in Russia.”
Reserves and other specially protected natural areas
To preserve a favorable habitat for rare animal species, humanity is creating places that are more carefully protected.
These include:
- protected areas;
- health resorts;
- natural parks;
- natural monuments;
- botanical gardens;
- nature reserves;
- arboretum zones;
- National parks.
The Krasnoyarsk region has 7 types of nature reserves. The lands of the Sayano-Shushensky, Taimyr, and Central Siberian reserves are considered biosphere reserves. They operate in accordance with a special UN program. There is a national park called “Shushensky Bor”. There is also a natural park, which was given the name “Ergaki”.
There are sanctuaries of federal significance (3), as well as 27 sanctuaries of regional significance. It is planned to establish a protected natural area in the amount of 39 pieces. In this region there are rare natural monuments that have reached regional significance (51 pieces).
Population
2,876,360 people live in the Krasnoyarsk Territory. 77% of all residents of the region are concentrated in cities. There are 1,700 rural and urban settlements here. The number of inhabitants per 1 km2 of territory is 1.21 people. This region is inhabited by people of various nationalities. The Russians are in first place.
Also, people from:
- Ukraine;
- Tatarstan;
- Germany;
- Azerbaijan;
- Belarus;
- Chuvashia;
- Armenia;
- Kyrgyzstan;
- Uzbekistan;
- Tajikistan;
- Mordovia;
- Republic of Mari El;
- Bashkortostan;
- You you;
- Lezgins;
- Moldova;
- Estonia;
- Latvia;
- other countries (persons who did not indicate nationality).
Table of regions of Russia. List as of 2022
There are 85 regions in Russia, including 22 republics, 9 territories, 46 regions, 3 federal cities, 1 autonomous region, 4 autonomous districts (Nenets, Chukotka, Yamalo-Nenets and Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra).
There are also 86 positions on the lists - code 99 - Other territories, including the city and the Baikonur cosmodrome - are not a region of the Russian Federation.
List of regions alphabetically
| № | The subject of the Russian Federation | Flag | Territory (km²) | Population _ | Admin. center | Municipalities |
Republic | ||||||
| 1 | Adygea | 7792 | ↗453 376 | Maykop | 7 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 2 | Altai | 92903 | ↗218 063 | Gorno-Altaisk | 10 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 3 | Bashkortostan | 142947 | ↘4 063 293 | Ufa | 54 municipal districts, 9 urban districts | |
| 4 | Buryatia | 351334 | ↗984 511 | Ulan-Ude | 21 municipal districts, 2 urban districts | |
| 5 | Dagestan | 50270 | ↗3 063 885 | Makhachkala | 42 municipal districts, 10 city districts | |
| 6 | Ingushetia | 3628 | ↗488 043 | Magas | 4 municipal districts, 4 city districts | |
| 7 | Kabardino-Balkaria | 12470 | ↗865 828 | Nalchik | 10 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
| 8 | Kalmykia | 74731 | ↘275 413 | Elista | 13 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 9 | Karachay-Cherkessia | 14277 | ↘466 305 | Cherkessk | 10 municipal districts, 2 urban districts | |
| 10 | Karelia | 180520 | ↘622 484 | Petrozavodsk | 16 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 11 | Komi | 416774 | ↘840 873 | Syktyvkar | 15 municipal districts, 5 urban districts | |
| 12 | Crimea | 26081 | ↗1 913 731 | Simferopol | 14 municipal districts, 11 city districts | |
| 13 | Mari El | 23375 | ↘682 333 | Yoshkar-Ola | 14 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
| 14 | Mordovia | 26128 | ↘805 056 | Saransk | 22 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 15 | Sakha (Yakutia) | 3083523 | ↗964 330 | Yakutsk | 34 municipal districts, 2 urban districts | |
| 16 | North Ossetia Alania | 7987 | ↘701 765 | Vladikavkaz | 8 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 17 | Tatarstan | 67847 | ↗3 894 284 | Kazan | 43 municipal districts, 2 urban districts | |
| 18 | Tyva | 168604 | ↗321 722 | Kyzyl | 17 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 19 | Udmurtia | 42061 | ↘1 513 044 | Izhevsk | 25 municipal districts, 5 city districts | |
| 20 | Khakassia | 61569 | ↘537 513 | Abakan | 8 municipal districts, 5 urban districts | |
| 21 | Chechnya | 15647 | ↗1 436 981 | Grozny | 17 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 22 | Chuvashia | 18343 | ↘1 231 117 | Cheboksary | 21 municipal districts, 5 urban districts | |
| The edges | ||||||
| 23 | Altai region | 167996 | ↘2 350 080 | Barnaul | 60 municipal districts, 11 city districts | |
| 24 | Transbaikal region | 431892 | ↘1 072 806 | Chita | 31 municipal districts, 4 urban districts | |
| 25 | Kamchatka Krai | 464275 | ↗315 557 | Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky | 11 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
| 26 | Krasnodar region | 75485 | ↗5 603 420 | Krasnodar | 37 municipal districts, 7 urban districts | |
| 27 | Krasnoyarsk region | 2366797 | ↗2 876 497 | Krasnoyarsk | 44 municipal districts, 17 urban districts | |
| 28 | Perm region | 160236 | ↘2 623 122 | Permian | 42 municipal districts, 6 city districts | |
| 29 | Primorsky Krai | 164673 | ↘1 913 037 | Vladivostok | 22 municipal districts, 12 city districts | |
| 30 | Stavropol region | 66160 | ↘2 800 674 | Stavropol | 26 municipal districts, 9 urban districts | |
| 31 | Khabarovsk region | 787633 | ↘1 328 302 | Khabarovsk | 17 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
Regions | ||||||
| 32 | Amur region | 361908 | ↘798 424 | Blagoveshchensk | 20 municipal districts, 8 urban districts | |
| 33 | Arhangelsk region | 589913 | ↘1 155 028 | Arkhangelsk | 19 municipal districts, 7 urban districts (without Nenets Autonomous Okrug) | |
| 34 | Astrakhan region | 49024 | ↘1 017 514 | Astrakhan | 11 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 35 | Belgorod region | 27134 | ↘1 549 876 | Belgorod | 19 municipal districts, 3 urban districts | |
| 36 | Bryansk region | 34857 | ↘1 210 982 | Bryansk | 27 municipal districts, 6 city districts | |
| 37 | Vladimir region | 29084 | ↘1 378 337 | Vladimir | 16 municipal districts, 5 city districts | |
| 38 | Volgograd region | 112877 | ↘2 521 276 | Volgograd | 32 municipal districts, 6 city districts | |
| 39 | Vologda Region | 144527 | ↘1 176 689 | Vologda | 26 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 40 | Voronezh region | 52216 | ↘2 333 768 | Voronezh | 31 municipal districts, 3 urban districts | |
| 41 | Ivanovo region | 21437 | ↘1 014 646 | Ivanovo | 21 municipal districts, 6 urban districts | |
| 42 | Irkutsk region | 774846 | ↘2 404 195 | Irkutsk | 27 municipal districts, 9 urban districts | |
| 43 | Kaliningrad region | 15125 | ↗994 599 | Kaliningrad | 15 municipal districts, 7 urban districts | |
| 44 | Kaluga region | 29777 | ↘1 012 156 | Kaluga | 24 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 45 | Kemerovo region | 95725 | ↘2 694 877 | Kemerovo | 18 municipal districts, 16 urban districts | |
| 46 | Kirov region | 120374 | ↘1 283 238 | Kirov | 39 municipal districts, 6 urban districts | |
| 47 | Kostroma region | 60211 | ↘643 324 | Kostroma | 24 municipal districts, 6 city districts | |
| 48 | Kurgan region | 71488 | ↘845 537 | Mound | 24 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 49 | Kursk region | 29997 | ↘1 115 237 | Kursk | 28 municipal districts, 5 city districts | |
| 50 | Leningrad region | 83908 | ↗1 813 816 | St. Petersburg[7] | 17 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 51 | Lipetsk region | 24047 | ↘1 150 201 | Lipetsk | 18 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 52 | Magadan Region | 462464 | ↘144 091 | Magadan | 8 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 53 | Moscow region | 44329 | ↗7 503 385 | Moscow[8], government in Krasnogorsk | 16 municipal districts, 51 urban districts (46 cities and 5 ZATOs), from 2022 56 urban districts and 11 municipal districts | |
| 54 | Murmansk region | 144902 | ↘753 557 | Murmansk | 5 municipal districts, 14 urban districts | |
| 55 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | 76624 | ↘3 234 752 | Nizhny Novgorod | 48 municipal districts, 4 city districts | |
| 56 | Novgorod region | 54501 | ↘606 476 | Velikiy Novgorod | 21 municipal districts, 1 urban district | |
| 57 | Novosibirsk region | 177756 | ↗2 788 849 | Novosibirsk | 30 municipal districts, 5 urban districts | |
| 58 | Omsk region | 141140 | ↘1 960 081 | Omsk | 32 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 59 | Orenburg region | 123702 | ↘1 977 720 | Orenburg | 35 municipal districts, 9 urban districts | |
| 60 | Oryol Region | 24652 | ↘747 247 | Eagle | 24 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
| 61 | Penza region | 43352 | ↘1 331 655 | Penza | 27 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
| 62 | Pskov region | 55399 | ↘636 546 | Pskov | 24 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 63 | Rostov region | 100967 | ↘4 220 452 | Rostov-on-Don | 43 municipal districts, 12 city districts | |
| 64 | Ryazan Oblast | 39605 | ↘1 121 474 | Ryazan | 25 municipal districts, 4 city districts | |
| 65 | Samara Region | 53565 | ↘3 193 514 | Samara | 27 municipal districts, 10 city districts | |
| 66 | Saratov region | 101240 | ↘2 462 950 | Saratov | 38 municipal districts, 4 city districts | |
| 67 | Sakhalin region | 87101 | ↗490 181 | Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk | 1 municipal district, 17 urban districts | |
| 68 | Sverdlovsk region | 194307 | ↘4 325 256 | Ekaterinburg | 5 municipal districts, 68 urban districts | |
| 69 | Smolensk region | 49779 | ↘949 348 | Smolensk | 25 municipal districts, 2 city districts | |
| 70 | Tambov Region | 34462 | ↘1 033 552 | Tambov | 23 municipal districts, 7 urban districts | |
| 71 | Tver region | 84201 | ↘1 283 873 | Tver | 36 municipal districts, 7 urban districts | |
| 72 | Tomsk region | 314391 | ↘1 078 280 | Tomsk | 16 municipal districts, 4 urban districts | |
| 73 | Tula region | 25679 | ↘1 491 855 | Tula | 23 municipal districts, 3 urban districts | |
| 74 | Tyumen region | 1464173 | ↗3 692 400 | Tyumen | 21 municipal districts, 5 urban districts (without Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Okrug) | |
| 75 | Ulyanovsk region | 37181 | ↘1 246 618 | Ulyanovsk | 21 municipal districts, 3 urban districts | |
| 76 | Chelyabinsk region | 88529 | ↘3 493 036 | Chelyabinsk | 27 municipal districts, 16 city districts | |
| 77 | Yaroslavl region | 36177 | ↘1 265 684 | Yaroslavl | 17 municipal districts, 3 city districts | |
Federal cities | ||||||
| 78 | Moscow | 2561 | ↗12 506 468 | Moscow | 146 intra-city municipalities (125 districts, 2 city districts, 19 settlements) | |
| 79 | Saint Petersburg | 1403 | ↗5 351 935 | Saint Petersburg | 111 intra-city municipalities (81 municipal districts, 9 cities and 21 villages) | |
| 80 | Sevastopol | 864 | ↗436 670 | Sevastopol | 10 intra-city municipalities (9 municipal districts, 1 city) | |
Autonomous region | ||||||
| 81 | Jewish Autonomous Region | 36271 | ↘162 014 | Birobidzhan | 5 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
Autonomous okrugs | ||||||
| 82 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | 176810 | ↗43 997 | Naryan-Mar | 1 municipal district, 1 urban district | |
| 83 | Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra | 534801 | ↗1 655 074 | Khanty-Mansiysk | 9 municipal districts, 13 urban districts | |
| 84 | Chukotka | 721481 | ↘49 348 | Anadyr | 6 municipal districts, 1 city district | |
| 85 | Yamalo-Nenets | 769250 | ↗538 547 | Salekhard | 7 municipal districts, 6 urban districts |
Table of regions of Russia in order of increasing code
| Code | Name |
| 01 | Republic of Adygea (Adygea) |
| 02 | Republic of Bashkortostan |
| 03 | The Republic of Buryatia |
| 04 | Altai Republic |
| 05 | The Republic of Dagestan |
| 06 | The Republic of Ingushetia |
| 07 | Kabardino-Balkarian Republic |
| 08 | Republic of Kalmykia |
| 09 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia |
| 11 | Komi Republic |
| 12 | Mari El Republic |
| 13 | The Republic of Mordovia |
| 14 | The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) |
| 15 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania |
| 16 | Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan) |
| 17 | Tyva Republic |
| 18 | Udmurt republic |
| 19 | The Republic of Khakassia |
| 20 | Chechen Republic |
| 21 | Chuvash Republic - Chuvashia |
| 22 | Altai region |
| 23 | Krasnodar region |
| 24 | Krasnoyarsk region |
| 25 | Primorsky Krai |
| 26 | Stavropol region |
| 27 | Khabarovsk region |
| 28 | Amur region |
| 29 | Arhangelsk region |
| 30 | Astrakhan region |
| 31 | Belgorod region |
| 32 | Bryansk region |
| 33 | Vladimir region |
| 34 | Volgograd region |
| 35 | Vologda Region |
| 36 | Voronezh region |
| 37 | Ivanovo region |
| 38 | Irkutsk region |
| 39 | Kaliningrad region |
| 40 | Kaluga region |
| 41 | Kamchatka Krai |
| 42 | Kemerovo region |
| 43 | Kirov region |
| 44 | Kostroma region |
| 45 | Kurgan region |
| 46 | Kursk region |
| 47 | Leningrad region |
| 48 | Lipetsk region |
| 49 | Magadan Region |
| 50 | Moscow region |
| 51 | Murmansk region |
| 52 | Nizhny Novgorod Region |
| 53 | Novgorod region |
| 54 | Novosibirsk region |
| 55 | Omsk region |
| 56 | Orenburg region |
| 57 | Oryol Region |
| 58 | Penza region |
| 59 | Perm region |
| 60 | Pskov region |
| 61 | Rostov region |
| 62 | Ryazan Oblast |
| 63 | Samara Region |
| 64 | Saratov region |
| 65 | Sakhalin region |
| 66 | Sverdlovsk region |
| 67 | Smolensk region |
| 68 | Tambov Region |
| 69 | Tver region |
| 70 | Tomsk region |
| 71 | Tula region |
| 72 | Tyumen region |
| 73 | Ulyanovsk region |
| 74 | Chelyabinsk region |
| 75 | Transbaikal region |
| 76 | Yaroslavl region |
| 77 | Moscow |
| 78 | Saint Petersburg |
| 79 | Jewish Autonomous Region |
| 83 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| 86 | Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra |
| 87 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug |
| 89 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug |
| 91 | Republic of Crimea |
| 92 | Sevastopol |
| 99 | Other territories, including the city and Baikonur cosmodrome |
Save it for yourselfPrint
0
Author of the publication
offline 4 hours
Your K.G.
285
In my free time I put things in order on this site
Comments: 127 Publications: 1748 Registration: 02/12/2016
Administrative division
There are 1,763 settlements in the region.
These include:
- large residential settlements (cities) – 23 pcs.;
- 1 p.g.t. (Urban-type settlement);
- rural areas in the amount of 1701 units;
- workers' settlements (35);
- residential settlements that are neither workers' settlements nor urban-type settlements, but which are classified as urban districts (2);
- residential settlements that are neither workers' settlements nor urban-type settlements, but which are classified as a city or urban-type settlement (1).
Norilsk, Krasnoyarsk, Achinsk, and Minusinsk play a fundamental role in economic development.
The main settlement of this region is Krasnoyarsk.
What is this
There is no definition of the concept in the Constitution, that is, they are not part of the administrative-territorial division of the state. The creation took place according to the principle of the formation of military districts and economic regions, but does not coincide with them either in number or composition. We can say that the federal district is a large territory, which includes several subjects of the state.
Economy
Rare components of the natural environment are concentrated in the Krasnoyarsk Territory, so industry here is at a high level.
Nickel, copper, primary aluminum, and platinum group metals are produced. The region is in 1st position in gold mining in the Russian Federation. The majority of the gross regional product comes from forest processing, mining and beneficiation of non-ferrous metal ores, mining, production, transmission and sales of electricity.
The use of electricity in this area, products of agriculture, forestry, fishing, a decent level of development of mines and mines are the main advantages of the regional economy. This territory in most cases has good production results.
The Krasnoyarsk Territory is on the list of 15 Russian regions that provide 70% of the exchange of goods of the Russian Federation with other states.
The region's terrain is covered by 2/3 forests.
There are large reserves of water and many unique natural resources. These indicators push the region to a leading position in sending industrial goods to neighboring regions and countries. Every year the number of industrial products increases by 3-6%, which allows us to judge the reliable economic development of the region.
Map of federal districts
For convenient familiarization with the territory occupied by the federal districts, appropriate geographical maps have been developed. You can find them in special atlases or on online resources. Among the latter, a good option is the site https://geostudy.ru/fo.html.
The convenience of maps lies in the fact that in addition to boundaries and occupied area, you can see the location of cities and other settlements, as well as geographical features - the location of reservoirs, forests, mountains, agricultural land, and so on.
Education
The main advantages of the Krasnoyarsk education system:
- high level of teaching;
- working with talented children;
- regular improvement of the qualification level of employees of the education system.
There are 1,053 institutions offering preschool education services, more than 1,400 institutions with full-time education (in cities - 447, in rural areas - 954), more than 200 educational institutions providing additional training for children, 89 institutions for children in primary school, as well as 63 educational institutions for children studying in secondary classes.
There are gymnasiums here: women's and cadet. Special knowledge in the field of education and science is concentrated in the Federal Research Center KSC SB RAS, as well as in some other institutions. Krasnoyarsk State Art Institute belongs to the field of culture. This industry also includes the Krasnoyarsk State Academy of Music and Theater.
Most large universities are concentrated in the main city of the region - Krasnoyarsk. Bachelors, specialists and masters are graduated here. The institutions have more than 330 specialties, which are taught by 92 thousand students.
Culture and attractions
The Krasnoyarsk Territory, which occupies a vast territory on the map of Russia, has over 4,500 historical and artistic monuments. Evidence of the first signs of the life of primitive man are the mounds of the Minusinsk Basin, the Shalobolinskaya Pisanitsa, and the ruins of fortifications that served to defend the city.
Libraries
The largest library in the region stores books (handwritten and printed in the old way), unique publications on local history, famous printed publications that were previously in the library of G. Yudin (merchant bibliophile).
There are 1,181 libraries in the Krasnoyarsk region. They are divided into municipal and state. Modern library workers organize fascinating lectures for children, telling about the culture of their native land and its influence on human life.
Theaters
In the mid-19th century, artists began to appear in Siberia, touring cities and other populated areas. In 1873 the first theater was built. It was made of wood. After 2 years, a theater group was created, led by D. Egorov. In 1898 the building was destroyed by fire. Later, the People's House Theater was created in Minusinsk.
In the 40s In the 20th century, a theater was founded in the village of Norillag. Convicts and artists of the 1st Polar Theater of 1936 worked there. There are 12 theaters, folk and academic ensembles, and festivals are held here. The Norilsk Polar Drama Theater named after. Mayakovsky, which has no analogues in the Russian Federation.
Museums
A large number of museums are concentrated in the Krasnoyarsk Territory. The region is in 1st place among all museums in Siberia.
N. Martyanov opened the Minusinsk Museum of Local Lore in 1877. 6 years later, the Yeniseisk Museum was built. In 1889, the largest museum in the country was created - the Krasnoyarsk Museum of Local Lore. Its analogues were created in Yakutsk, Irkutsk, Yeniseisk and some other settlements of Siberia.
In Igarka there is the only permafrost museum in the world. Only here there is an empty space underground inside the soil, which has been frozen for centuries.
Sport
Every year the number of residents of the Krasnoyarsk Territory involved in physical activity increases. However, physical activity levels are still low.
The population does not feel the need for regular sports activities. Today, even 40% of the region’s residents do not exercise regularly. For disabled people and people with health problems, this figure is 7.2% of their number.
To bring sports to a higher level, 127 physical education and sports organizations have been created in this region. The regional government sets itself the task of introducing the correct lifestyle and physical exercises for people of different age categories into the cultural development of society.
Tourism
At the end of the 20th century, a motor ship consisting of 4 decks was rebuilt. From that moment on, people began to go on cruises along the Yenisei River. But soon the movement of the ship was transferred to the Volga.
The Krasnoyarsk region receives many travelers (the region occupies a central place on the Russian map). Tourists visit the Shushenskoe and Sayan Ring (international festival of ethnic music), as well as the famous drag racing competition. In this industry, many victories have been achieved by Russian participants.
Monuments
There are 7 main monuments of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, striking in their originality:
- Monument to A. Dubensky (Krasnoyarsk).
- Eiffel Tower (Krasnoyarsk).
- Monument to the chair (Norilsk).
- Monument “Bogatyrs of Russia” (Zheleznogorsk).
- Monument to a girl geologist (Norilsk).
- Wall to those killed in the Second World War (Zelenogorsk).
- Monument “Tsar Fish” (Krasnoyarsk).
Golden fever
Gold mining in the Yenisei province began in the 30s of the 19th century. The discovery of mines took place along the rivers Upper and Lower Tunguska, Biryusa, Mana and their tributaries. Gold was found even in Krasnoyarsk itself on the Bugach River, on Afontovaya Mountain, prospectors panned for gold on Stolby. A lot of people worked in the mines, for example, almost 6,000 people were hired at Mariinsky in 1840, 90% of whom were exiled settlers.
There was a leap in manufacturing and agriculture. In 1859, 2 million poods of grain and 15 thousand heads of cattle were supplied to the mines of the Yenisei province alone, and the production and sale of fish increased threefold. What was needed were horses, their harness, carts and equipment, which were manufactured in the city.
The construction of houses, which to this day serve as the decoration of the city, increased sharply; new squares and churches appeared in Krasnoyarsk. In 1863 a telegraph station was opened. In the same year, steamships started sailing along the Yenisei. A men's gymnasium was built in 1868, and 10 years later a women's gymnasium. A paramedic school was opened. Primary schools started working.
Religion
There are about 270 religious organizations in the Krasnoyarsk Territory. The main religion of the local population is Orthodoxy.
Registered here:
- Armenian Apostolic Church;
- Old Believer organization;
- Roman Catholic churches;
- true Orthodox churches;
- Protestant denominations;
- Muslim organizations;
- Buddhist organizations;
- Jewish organizations;
- organizations of Jehovah's Witnesses.
On the map of the country, the Krasnoyarsk Territory occupies a significant territory. In the modern world, the region is an important part of Russian education, economy and industry.
Author: Ekaterina Pisarenko
Article design: Vladimir the Great