Year founded: 1955
City Day is celebrated
on December 12
.
Hotel "Taiga" (Photo: S. Anisimov)
Bratsk
- a city in the Irkutsk region of Russia, located 490 km north of Irkutsk, in the center of the Angarsk Ridge, on the shore of the Bratsk Reservoir.
Historical reference
. A small fortress on the Angara River at the mouth of the Oka River was founded by Cossack explorers in 1631 and called it the Bratsk fortress. The origin of the name is explained by the Russian reinterpretation of the Buryat ethnonym into “brothers” - “brothers”.
After losing its military significance, the fort turned first into the village of Bratsko-Ostrozhnoe, then simply into Bratskoye and, finally, into Bratsk.
Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station (Photo: www.bratsk-city.ru) In 1927, the Bratsk fort became the center of the Bratsk district of the Tulun district. In 1946, the Council of People's Commissars adopted the “Resolution on the organization of the Angarsk construction management.” In the fall of 1954, a resolution was adopted on the construction of the Bratsk hydroelectric power station. Thus began the construction of the Bratsk hydroelectric power station and the city of Bratsk. The site soon becomes an all-Union construction site.
In March 1957, the first closure of the Angara was completed, and in the summer of 1961 the filling of the Bratsk Reservoir began. Finally, on September 1, 1961, a historical event occurred - the birth of the Brotherly Sea. The village of Bratsk is flooded along with many other villages - in the Bratsk region alone, 119 settlements were resettled and went under water.
Near the drama theater (Photo: G. Taraskov)
The village of Bratsk itself was moved to a new location and, back in 1951, transformed into a workers’ village. In 1955, it was merged with a number of other villages and transformed into the city of Bratsk on December 12, 1955.
Today
Bratsk is one of the largest industrial centers of the Irkutsk region and Eastern Siberia. And although the city is located in harsh climatic conditions, its economic and geographical position is relatively favorable and is characterized by developed infrastructure.
Railway (Baikal-Amur Mainline), roads, power lines, an airport with international status, high resource and economic potential, electric power resources of the Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station, unlimited water resources, shipping and timber rafting routes - Bratsk functions as an important support base for the development of the northern regions of Eastern Siberia and the Far East.
Night city (Photo: G. Taraskov)
The permanent population of Bratsk is more than 225 thousand people (2021). Mostly young people live here. The average age of city residents is 36 years, and children under 16 make up about 18%.
Not far from Bratsk, 60 km to the east, there is the Bratsk Seaside, a climatic resort area on the coast of the Bratsk Reservoir, where patients with diseases of the circulatory system and nervous system are treated. This is also facilitated by sodium sulfate-chloride water, found here in 1976.
Day of the city
dedicated to the day of its foundation and celebrated on December 12.
Characteristics of the city of Bratsk, Irkutsk region
Today, Bratsk on the map of Russia is a city in the north-west of the Irkutsk region in the central part of the Angara Ridge , the districts and sections of which are located at large distances, separated by forest plantations and water spaces. It forms the administrative center, the urban district. This unique shape of the city is explained by its origin - Bratsk was a union of villages and towns located near the Angara River .
The current population is about 230,000 inhabitants. Bratsk is located in the center of the East Siberian economic region of the Russian Federation, near the Bratsk reservoir , and this allowed it to become the intersection of automobile, railway, air, and waterways leading to Europe and Asia, as well as Siberia and Yakutia. Thanks to these factors, Bratsk has become a strategically important, economically developed city.
Population
In terms of population, Bratsk ranks second among the cities of the Angara region (after Irkutsk and Angarsk).
The city is home to 249.7 thousand people, which is about 10% of the population of the Irkutsk region (as of 2010). The dynamics of the number of residents is shown in table. 23.
Table 23. Population dynamics of Bratsk, thousand people.
| 1959 | 1967 | 1970 | 1980 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 |
| 51,0 | 122,0 | 155,4 | 218,1 | 277,6 | 256,6 | 249,7 |
Table 24. Population structure of Bratsk in 2005, %
| Population category | Share in total number |
| Men | 45,4 |
| Women | 54,6 |
| Children and schoolchildren | 17,3 |
| Working population | 64,3 |
| Pensioners | 18,4 |
| Total | 100,0 |
In the last decade, the population of Bratsk decreased annually by 0.5-1.5 thousand people, mainly due to natural decline (the number of deaths exceeded the number of births by 1.3-1.4 times), as well as due to the large migration outflow (about 500 people left the city annually).
The share of men in Bratsk is 45.4%, women - 54.6%. 17.3% of residents are younger than working age, 64.3% are of working age (Table 24). The average age of the population is about 40 years (as of 2009). There is an increase in the share of adults and elderly people, while the share of children and youth is decreasing.
The city’s economy employs 97.5 thousand people, which is about 60% of the economically active population. Just over 80 thousand people are employed in enterprises and organizations, including about 40% in industry, 30% in the public sector, and 30% in other industries (including small businesses).
Historical facts of the city
- From 1630 to 1648, the Bratsk fort was built, which served to gather troops, had a defensive function, and was a place for the exchange of goods.
- The entire 17th century belonged to the Yenisei fort, gradually changing the name to the modern one. There is a confident development of trade routes and the economy.
- In 1917, Soviet power was established in the city.
- The most important point is the construction of the Bratsk hydroelectric power station in 1955, which became the point of uniting nearby settlements under one name, blocking the Angara, and creating a reservoir.
Number of residents of urban settlements
| Settlement | Number of registered residents |
| Markova | 23672 |
| Chunsky | 14135 |
| Zalari | 9 576 |
| New Igirma | 9 496 |
| Kuitun | 9 487 |
| Belorechensky | 7 643 |
| Mikhailovka | 7 478 |
| Kachuk | 6 950 |
| Railway | 6 463 |
| Trunk | 6 053 |
| Mishelevka | 5 260 |
| Yurts | 5 247 |
| Thelma | 5 136 |
| Zhigalovo | 4 983 |
| Lesogorsk | 4 982 |
| October | 4 952 |
| Average | 4 909 |
| Ulkan | 4 719 |
| Taiturka | 4 614 |
| Novobiryusinsky | 4 463 |
| Tyret First | 3 944 |
| Kultuk | 3 715 |
| Rudnogorsk | 3 198 |
| Big River | 2 936 |
| Mother | 2 851 |
| Ticket | 2 712 |
| Shumsky | 2 530 |
| Alekseevsk | 2 157 |
| Listvyanka | 1 972 |
| Shitkino | 1 786 |
| Mamakan | 1 640 |
| Uk | 1 593 |
| Atagay | 1 569 |
| Yantal | 1 543 |
| Khrebtovaya | 1 268 |
| Artemovsky | 1 253 |
| We see | 1 108 |
| Kropotkin | 1 102 |
| Balakhninsky | 1021 |
| Yangel | 984 |
| Radishchev | 956 |
| Star | 854 |
| Shestakovo | 606 |
| Lugovsky | 367 |
| Vitimsky | 260 |
| Kunerma | 0 |
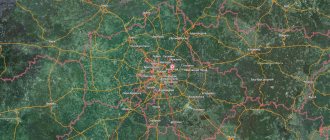
Bratsk on the map of Russia: geography, nature and climate
When looking at a map of Bratsk from a satellite, it becomes clear why, with a territory of about 428 square kilometers, the city’s population is only 230,000 people - the area consists of “islands” of settlements. On the shore of the reservoir, the length of Bratsk is about 65 km, and to the regional center - Irkutsk - 460 km.
The climate in this area is quite harsh - long winters, in which the thermometer often drops below -35°C, and in the summer - rather hot short periods, when the temperature is about +30°C.
Bratsk belongs to the Far North, here the climate is sharply continental, the usual amount of annual precipitation is about 370 mm.
Maximum historical temperatures and precipitation:
- Minimum temperature - -51°C
- Maximum temperature +36°C
The city is surrounded and even divided into sections by mountain ranges, due to which the entire area is located on a hill. The most important role is played by water areas - in addition to the Bratsk reservoir, there is the Ust-Ilimskoye, the Angara and Vikhoreva .
METALLURGIST PARK
Although I have lived in Bratsk since 1985, I somehow never had the opportunity to visit the park in central Bratsk. I even thought he wasn't there. And when I got ready to write about cultural and entertainment centers, I was surprised to read that they still exist. And I went in search of him. I took a trolleybus to the Baikal shopping center, walked forward a little and turned right. Then I had to walk half a kilometer along the street past individual houses and, finally, behind a small, unkempt public garden, I saw the iron lattice fence of a park with the proud name “Metallurgists’ Park.”
But this park didn't look like a park at all. For the most part, this is a long wide asphalt strip along which children rode scooters. Along this asphalt road there were carousels and similar private attractions for small children, as well as gazebos and kiosks. A park primarily implies trees, but there were almost none there.
True, there was one single alley along the fence, which attracted my attention: there were many sculptures of fairy-tale characters on it. The sculptures are made very well, with imagination and are very recognizable. There were Cheburashka with the crocodile Gena, and Pinocchio with Karabas Barabas, and the Little Mermaid, and Funtik, and Baba Yaga, and Bogatyr, and Kuzya the Brownie, and even the inseparable trinity Vitsin, Morgunov and Nikulin and many other characters. Here's everything you can see in the park.
Routes on the map of Bratsk. Transport infrastructure
The city is a major transport hub, connecting all types of routes. Bratsk is connected by important highways:
- Federal highway A-331 "Vilyuy" starts in Tulun from the highway R-255 "Siberia" and passes through Bratsk, Ust-Kut, Mirny to Yakutsk,
- public highway 25N-124 Taishet - Chuna - Bratsk ,
- intermunicipal road 25N-126 Bratsk - Ust-Ilimsk .
The city has its own Bratsk airport , which has international status, but is not very conveniently located - 8 kilometers north of the city limits.
The railway tracks are aimed at connecting with the largest cities in Russia and abroad and are united by stations, each of which is located in one of three districts of the city:
- Central district - Anzebi railway station , address Dorozhnaya, 23a. Long-distance trains to Moscow, Neryungri, Ulan-Ude, Irkutsk, Ust-Ilyimsk, Severobaikalsk pass through the station. Suburban electric trains: Vikhorevka, Rechushka, Kezhemskaya.
- Novobratsk railway station is located in the Central region between the bus station and the Central market. Receives electric trains in the direction of Vikhorevka, Bagulnaya-2, Kezhemskaya
- Stroitel village - Bratsk railway station . Receives commuter trains in the direction of Novobratsk, Bagulnaya-2, Vikhorevka, Kezhemskaya.
- Padunsky district - station complex Padunskie Porogi , address Energetik village, Mechtateley street 30. Receives long-distance trains to Moscow, Neryungri, Anapa, Tynda, Ulan-Ude, Ust-Ilyimsk, Severobaikalsk. Suburban trains: Vikhorevka, Kezhemskaya, Rechushka
- Pravoberezhny district - Gidrostroitel railway station , address Osinovka village, Zheleznodorozhnaya street 8. Suburban trains: Vikhorevka, Kezhemskaya, Rechushka
Social transport in Bratsk is represented by buses, minibuses and trolleybuses, served by three private and three municipal organizations. This area is in a state of constant modernization due to the needs of local residents, but does not keep pace with the growth of the city - about 80% of the entire vehicle fleet is in a state of wear and tear.
In the southern part of the Central district, at st. River Port, 1, the Bratsk River Port is located, carrying passengers from June 2 to September 22 on the route Balagansk - Bratsk and back (Stops: Balagansk, Ust-Uda, Anosovo, Chisty, Shumilovo, Bratsk).
Energy
This industry is represented by three large enterprises owned by Irkutskenergo - Bratsk HPP, CHPP-6 and CHPP-7 (Table 28).
Bratsk hydroelectric power station. Its construction was due to the presence of significant hydropower resources in the Angara and the tasks of accelerated development of the eastern regions of the country. The launch of the first power unit took place on November 28, 1961. Currently, 18 units of the station annually generate 30 billion kWh of electricity (with a design value of 22.6 billion). Since the beginning of operation, the hydroelectric power station has contributed about 1 trillion to the national economy. kWh of the cheapest electricity in the country.
Table 28. Characteristics of hydroelectric power stations and thermal power plants of the city of Bratsk
| Station | Power | Coal used as fuel | |
| Electric, MW | Thermal, Gcal. per hour | ||
| Bratsk hydroelectric power station | 4500 | — | — |
| CHPP-6 | 270 | 1529 | Irsha-Borodinsky |
| CHPP-7 | 6 | 462 | Irsha-Borodinsky, Pereyaslavsiy |
CHPP-6. This station was created as the main source of heat supply to the Bratsk forestry complex and the central part of the city. It is located on a limited area (14 hectares) within the BLPK. The first boiler was launched here in 1964. There is a coal warehouse with a capacity of 350 thousand tons. Boilers with liquid slag removal are installed.
CHPP-7. The station began to be built to supply heat to the enterprises of Bratskgesstroy, as well as the villages of Padun and Energetik during the construction of the Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station. The first boiler was launched in 1961, and five years later the station was transferred to Irkutskenergo. Nowadays it, together with several other heat sources, operates as part of the Bratsk heating networks (their total thermal capacity is 1061 Gcal per hour).
The stations have a certain reserve of electrical and thermal capacity, which allows increasing production volumes at existing enterprises and developing the city.
Sights of the city of Bratsk
- The Museum of the History of Political Exile on Parkovaya Street - 3 is a former church house, the theme of the museum is the history of exile and political prisoners.
- Architectural and Ethnographic Museum "Angarsk Village" on the street. Komsomolskaya-38 has exhibitions and reconstructions of the life of the indigenous inhabitants of the area - the Evenks, as well as historical elements of the development of the city.
- Catholic Church on the street. Kurchatov is a religious landmark of the city.
- Museum of the History of Bratskgesstroy on the street. Hydrostroiteley - 54 contains authentic samples of photographs, documents, materials telling about the construction of a local hydroelectric power station.
- At the Bratsk hydroelectric power station in the village of Energetik there are special observation platforms that offer views of the area and the Angara River.
- United Museum of the History of the Development of the Angara on the street. Komsomolskaya-38 consists of four branches, contains historical samples and materials about the past of local towns and settlements.
- The Drama Theater on Mira Street-37 is a historical landmark of the city.
Social sphere
There are more than 100 general educational institutions in the city (56 preschool, 47 secondary educational, 2 secondary specialized and 9 secondary vocational), as well as 13 institutions of additional education. They employ more than 4 thousand teachers. By the number of schools, Bratsk ranks second in the Irkutsk region, and by the number of kindergartens - third.
The Bratsk State University operates (created on the basis of the Bratsk Industrial Institute, which was later transformed into the Bratsk State Technical University). There are branches of Irkutsk universities (Baikal State University of Economics and Law, Irkutsk State University, Irkutsk State University of Transport), as well as branches and representative offices of a number of other universities in the country.
The Siberian Research Institute of Forestry and Pulp and Paper Industry operates (until 1992, known as the Research Institute of Pulp and Cardboard).
The cultural sphere is represented by a network of libraries located in all districts of Bratsk, as well as two city theaters (drama and puppet), three museums (historical and local history, political exile, architectural and ethnographic open-air - “Angarsk Village”). The Bratsk City United Museum of the History of the Development of the Angara was created. There is an art exhibition hall.
There are more than 20 healthcare institutions, including 5 large hospitals, 5 dispensaries, several dental clinics, emergency medical care, a blood transfusion station, a medical prevention center, etc.
There is a network of medical and recreational institutions - the Bratskoe Vzmorye sanatorium, the Solnyshko sanatorium, two children's sanatoriums - Ladushki and Podsnezhnik, the Yubileiny medical and recreational complex with a hospital for veterans, etc.
Bratsk is one of the largest sports centers in the Irkutsk region. There are 275 sports facilities here, including 81 gyms, 5 swimming pools and 4 stadiums. About 18% of the population (more than 40 thousand people) regularly engage in physical education and sports. 5 thousand schoolchildren (almost 19% of the child population) attend various sports sections.
The city has a ski complex “Angarskaya Gora”, which has two illuminated slopes (420 and 600 m) with two ski lifts (nearby there are recreation centers “Zdorovye”, “Yubileinaya”, etc.).
Bratsk is famous for its luge track, which has been operating since 1971. It has trained 12 international-class masters of sports, about 100 masters of sports of the USSR and Russia. Ten students of the fraternal luge school became winners and prize-winners of the world and European championships, 36 became champions of the USSR and Russia.
Main streets of Bratsk
Let's take a look at the map of Bratsk with houses and streets, here we can see the following large objects:
- Komsomolskaya Street - has a length of 3.1 km, originates from Yuzhnaya Street and heads northeast, crossing the street along the way. Yangel, Gagarin, Krupskaya. It houses the city administration, courthouse, market, and shopping center.
- st. Yangelya - has a curved shape, a total length of approximately 3.12 km. It starts and ends from Komsomolskaya Street, forming a semicircle to the west. Has an intersection with the street. Barkova, Ryabikova. A city hospital, several shopping malls, a police building, the Ministry of Emergency Situations, and a pre-trial detention center were built on it.
- Proletarskaya Street - has an approximate length of 2.1 km. It starts from Gidrostroiteley Street and is separated from it by a railway bridge, then it runs to the northwest, flowing into the A-331 highway. It has an intersection in the direction of Polevaya Street, Svoboda Street and smaller ones. It houses a bank, kindergarten, school and residential buildings.
- Yeniseiskaya Street is one of the longest streets in the city and has a gap, making its parts 5.17 km and 1.14 km respectively. The general direction is northwest, starting from Radishchev Street. It has an intersection with Vokzalnaya Street, Sosnovaya Street, Sholokhov Street, Manezhnaya Street and others, less significant. It houses a technical school building, kindergartens, an art and general education school, and industrial facilities.
- Mira Street - has a northern direction and a length of 5.04 km and is located in the city center. It has an intersection with South Street, Podbelsky, Obruchev, Gagarin. There is a market, a drama theater, schools, and a shopping center on it.
- St. Kurchatova - has a western direction, starting from Lomonosov Street, in the direction it intersects with Deputatskaya, Mira, Komsomolskaya, Ryabikova, ending with the A-331 highway. It has a total length of 4.1 km. It houses industrial facilities, a hospital, and a technical school.
Housing and communal services
The total area of the housing stock in Bratsk is 5248 thousand m2 (as of 2008), or 10.4% of the housing stock of the Irkutsk region. The main part (95%) is fully landscaped. It is planned to reconstruct the city water supply system, aimed at increasing underground water intake to 140 thousand m3 per day, introducing a system of reagent-free water disinfection, using polyethylene pipes (more than 50 km of networks), etc. At the same time, it is planned to reconstruct the complex of treatment facilities, designed to increase their throughput, and introduction of new wastewater treatment technologies. Modernization of these facilities will increase the reliability of the city water supply and sewerage system, reduce the likelihood of emergency situations, bring the quality of city wastewater to standard values, and make it possible to abandon chlorine disinfection of wastewater.
Popular message topics
- Email Email
is information stored on a computer that is transferred between two users via telecommunications. Simply put, email is a message that can contain text, files, - Tea
Tea (translated from Chinese “cha”, from the Beijing and Guangdian dialects - “te”) is a drink obtained by boiling, brewing or infusing tea tree leaves. The tea tree leaf undergoes special treatment before use. - City of Korolev
Everyone knows the great very first cosmonaut from the USSR, Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin, who on the Vostok-1 spacecraft made the world's first flight into such an unknown space at that time as space. Indeed, this man's name was