There are many beautiful cities in Russia. Most of them boast their attractions, rich history, beautiful nature, as well as various interesting facts. Each city has its own special atmosphere and has characteristic features unique to it. The wonderful city of Perm is no exception. It really deserves special attention, as it has a great historical and cultural heritage. The article will talk about the city itself, how old Perm is, its attractions and much more.
The city of Perm: general characteristics
This wonderful settlement is located in the European part of our country. The city is the administrative center of the Perm region. There is also a port here, which is located on the Kama River. Perm is a large city with a large number of inhabitants. As of 2016, the local population was 1,041,876 people, which is a fairly high figure. Perm received the status of a million-plus city back in the late 70s of the 20th century. Of course, many are interested in how old the city of Perm is. The answer to this question will be discussed a little later.
It is also worth saying that the settlement has important transport significance. In addition to the port, there is a large logistics hub here, since the city is located on the Trans-Siberian Railway. Many industries are also well developed here. However, the city is not only a production center, but also a scientific and cultural center.
Climate and ecology of Perm
The climate of Perm is temperate continental. The increased humidity is due to its location on the river and the proximity of the Kama Reservoir. A special feature of the geography of Perm is the presence of small rivers flowing within the city in ravines, and a huge number of urban forests that occupy a significant part of the city territory (almost 400 sq. km) and significantly improve the ecology of a large industrial center.
Snowy long winter with an average temperature of -15 -20 C. Moderately warm summer within the temperature range of +18 +23C.
The peculiarities of the climate of the Perm region include fairly frequent thunderstorms, fogs and snowstorms and inconsistent weather conditions (spring returns of cold weather, frosts in early summer, hail and summer showers).
Rainfall in Perm in 2011
The well-developed industry of the region and the presence of large enterprises determine the environmental problems of the region, the causes of which are both man-made pollution and insufficient environmental management.
The main sources of air pollution in Perm are emissions from industrial enterprises, to which increased vehicle emissions have been added in recent years with the growth of the vehicle fleet. Water bodies are polluted mainly due to the discharge of industrial wastewater.
By district of the city, emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere are distributed in the following order: Industrial (about 50%), Ordzhonikidze (about 20%), Sverdlovsk and Kirov (about 10% each), Dzerzhinsky and Motovilikha (about 4%) and 1% in Leninsky .
The solution to the problem is the modernization of production, which makes it possible to eliminate the threat of harmful emissions without loss of production capacity (carried out, for example, by the Perm Scientific and Production Instrument-Making Company, which produces navigation systems).
Photo by Igor Lugovoy
One of the problems of Perm is the presence of ticks in the forested areas of the city - carriers of tick-borne encephalitis. To protect the population, urban forests and park recreation areas are annually treated with special compounds, and medical institutions vaccinate against the disease.
Environmental projects with the participation of city enterprises and volunteers made it possible to clean more than 20 km of the banks of the city’s small rivers, improve parks and recreational areas, and plant hundreds of trees.
How old is Perm: when was the city founded?
Thus, we got acquainted with general information about this locality. Indeed, Perm is a large city whose history goes back many years. Many important events took place here. Of course, it’s worth talking about how old Perm is. It was founded in the 18th century by Vasily Tatishchev. If we talk about a more precise date, it happened in 1723. It turns out that the age of the city is 293 years. In 2023, Perm will celebrate its 300th anniversary. Of course, compared to other Russian cities, Perm is not such an old city, but it has a rich history, which will be discussed a little later.
It is interesting that for some period of time the settlement was called Molotov. This happened in the 40s of the 20th century. However, soon, in 1957, the city was renamed back.
Probably, many will be interested in the question of when is the day of the city of Perm. This holiday is celebrated every year on a certain day - June 12.
So, we got to know this beautiful city better, found out how old Perm is, as well as the date of its foundation. Of course, it is worth telling about the history of the city. It was always rich in various interesting events.
Top 10 Russian cities with the largest population
The largest cities in Russia are similar in size to the 15 leading cities in terms of area. The five first places are in the capital and cultural capital, Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod. The Top 10 ends with Omsk, Samara and Rostov-on-Don.
| № | City | Population, thousand people |
| 1 | Moscow | 12506 |
| 2 | Saint Petersburg | 5352 |
| 3 | Novosibirsk | 1613 |
| 4 | Ekaterinburg | 1469 |
| 5 | Nizhny Novgorod | 1259 |
| 6 | Kazan | 1244 |
| 7 | Chelyabinsk | 1202 |
| 8 | Omsk | 1172 |
| 9 | Samara | 1163 |
| 10 | Rostov-on-Don | 1130 |
Overall, the top ten has remained stable over the past decade. Cities with a population of over a million attract travelers from all over the country and the world, students, workers and just visitors. The statistics are compiled on the basis of the annual population census conducted by Rosstat.
In Russia, for every thousand cities there are dozens of the largest ones, many of them are included in the rankings every year due to their area and population. Moscow and St. Petersburg have remained the undoubted leaders for a long time. The top five largest cities by territory also include Volgograd, Perm and Ufa, and the 3rd, 4th and 5th millionaire cities are Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg and Nizhny Novgorod.
Author: Alex Reimers
Article design: Vladimir the Great
A little about the name of the city
The names of various settlements always cause special interest. From some of them it is easy to guess what word they came from. However, this is not always the case; sometimes it is impossible to understand the meaning of the name without turning to additional sources. Many people are so accustomed to the name “Perm” and do not think about what it means.
The word itself appeared in ancient times. It is believed that it originated from the Vepsian language. This is one of the branches of the Baltic-Finnish languages. The word means "distant land." Other versions of the origin of the word are also considered. One of them says that it came from the Komi-Permyak words “perema”, which means “far”, or “parma” (translated as “forest”). Now it becomes clear where the name of the city of Perm came from.
Ufa | 707 sq. kilometers
Ufa, whose territory is 707.93 square meters. kilometers, is in fifth place in the list of the largest Russian cities. The population has more than a million inhabitants. The capital of the Republic of Bashkortostan is a major cultural, scientific, economic and sports center of the country. The importance of Ufa was confirmed by the BRICS and SCO summits held here in 2015. Despite the fact that Ufa is a million-plus city, it is the most spacious settlement in Russia - there are almost 700 square meters per resident. meters of city territory. Ufa is considered one of the greenest cities in the country - there are a large number of parks and squares. It is also distinguished by a wide variety of monuments.
History of the city of Perm: how did it appear?
This area was inhabited long before the first settlements appeared here. Many archaeological excavations were carried out in Perm, as a result of which more than 100 different objects dating back to different times were found. In the 17th century, the territory where the city is now located belonged to the Stroganov merchants. There were several settlements here, for example, the village of Zaostrovka and a village called Verkhniye Mully.
The founding of Perm, as mentioned above, dates back to 1723. It was then that the construction of a copper smelter began here. I wonder what prerequisites existed here for the founding of the city? It is known that in 1720 V.N. went here. Tatishchev by order of Peter I. This was necessary in order to select a place for the future construction of various factories. He chose a village called Yegoshikha because it was here that there were reserves of copper ore.
The settlement also had a favorable transport location. After some time, the project was approved, and construction of the plant began here. Thus, it becomes clear when the settlement was founded and how old the city of Perm will be. We also found out what objects were in these places before the appearance of the city itself.
"A busy place"
As Pavel Korchagin convincingly writes in his book “The Provincial Capital of Perm,” the place at the mouth of Yegoshikha is a natural ideal pier, since it is here that for the first time after the confluence of the Kama and Chusovaya the navigable channel approaches the very shore. There are never shoals here, and navigation opens two weeks earlier than at Levshino. “The grain market and, accordingly, trade in other goods are beginning to move more and more from Kungur to Yegoshikha.”
Alexey Ivanov perfectly described what a dangerous event the rafting of “iron caravans” along Chusovaya was. After reaching the Kama, they inevitably had to stop to put themselves in order, take on new pilots who knew the difficult Kama fairway, change part of the crew, and re-sort the cargo.
It was the transport and logistics function that determined the development of Yegoshikhinskaya Sloboda - regardless of whether there was a plant here or not. Especially after the Siberian Highway through Kungur was finally officially opened in 1763. In the village of Yegoshikha, life now does not stop either in winter or in summer. The copper smelter is increasingly withering away.
After the end of the Pugachev War, it was decided to move the administrative division to smaller, more manageable provinces and governorships. It was proposed to make them up based on 300-400 thousand inhabitants. Among the new “subjects”, the Perm-Tobolsk governorship was established, consisting of districts of the Kazan and Siberian provinces. In the Perm governorship, two regions were created - Perm and Ekaterinburg.
By that time, Yekaterinburg was one of the largest settlements in the Urals and rightfully became the capital of the Trans-Ural region. In the Perm half, the center city was not even chosen. It could, for example, be Kungur. Or Solikamsk, the old capital of the Middle Urals.
To select a location, first a commission headed by Kazan Governor-General Platon Meshchersky arrived in the Urals, then Lieutenant General Evgeny Kashkin. For the Kazan governor, the Kama region was until recently a subordinate territory; his visit is understandable. But Kashkin was appointed governor-general of the entire Perm-Tobolsk governorship. Looking for a place for the center of the Perm region - only an integral part of his subject territory, he suddenly announced that he had found the best option for the location of the capital of the entire governorship - in Yegoshikha Sloboda.
“This settlement became, by its position, the main pier on the Kama... The turnover of this trade and the proximity of various... factories served as a reason... to build a settlement, more preferable than other cities located in this region.”
The Governor-General of Siberia, Chicherin, by that time was out of favor with Catherine II for being too unaccountable in governing this vast region and did not have a word. Nevertheless, Kashkin also visited Yekaterinburg. But for some reason I was not impressed and stood for Yegoshikha and Kama.
General Kashkin, and not Captain Tatishchev, is the hero who accomplished the incredible: he founded the provincial city of Perm.
Further history of Perm
Of course, it becomes interesting how the city developed further. Gradually the settlement developed. In 1780, Catherine II decided to create a new city, Perm, next to the existing plant. After this, the city began to be actively developed; buildings of various official institutions were erected here, roads were laid, and much more. Already in 1796, the Perm province was formed, the center of which was Perm.
Since then, the city began to develop even faster. At the end of the 19th century, construction of railways began here in several directions. Around the same time, various institutions related to art, culture and science began to open here. An opera and ballet theater was built, as well as the first cinema.
However, the revolution affected Perm, just like other Russian cities. This will be discussed a little later.
Paleolithic site Yegoshikha
One and a half ten thousand years BC, on the site of Perm there was a site of ancient people. She was called Yegoshikha. It got its name from the river of the same name that flowed nearby.
Nowadays, in 2003, before the construction of a gas station, archaeologists examined the construction site at Parkovaya 16, next to the northern dam.
Illustration from perm.vsedomarossii.ru
And they discovered amazing finds. Which confirmed the fact of the existence of a permanent settlement at this place.
Revolution and Soviet times
As you know, the history of the city of Perm includes many events. One of them is revolution. In 1917 it happened here too. On November 8, news arrived in the city that the October Revolution had begun. Initially, almost all representatives of the city council condemned this step. However, after some time, a congress was held at which the establishment of Soviet power was proclaimed.
After this event, the city's population grew significantly. From 1926 to 1939 the number of residents increased many times, from 84 thousand to 306 thousand people. And by 1970, Perm had become a million-plus city.
During the Great Patriotic War, the city actively participated in the fight against invaders. Most of the city's enterprises were used for military purposes. The production of various ammunition, weapons, and chemicals was organized here.
Enterprises and work in Perm
Perm's economy has traditionally been characterized by a developed heavy industry sector. The industrial traditions of the Kama region received a new direction during the Great Patriotic War. The region became one of the main regions where the population and enterprises working for military needs were evacuated. In the post-war years, the construction of industrial enterprises continued - in 1955 the Kama hydroelectric power station was built, in 1958 - the Perm oil refinery.
Lukoil Perm
The wealth of raw materials plays an important role in the potential development of the Perm region. The region has 10% of iron ore reserves and 25% of coal reserves in the Urals. The Verkhnekamskoye deposit of potassium salts is unique - the only place in the country where they are mined. The region contains deposits of rare earth and non-ferrous metals, gold and platinum. High-quality diamonds are also mined in the Kama region.
Thanks to the natural resources of the subsoil, the region's industry is represented by a powerful complex of enterprises in the main industries: metallurgy, mechanical engineering, petrochemical and mining industries, and timber processing.
Today, the leading position in the city's production is occupied by mechanical engineering and metallurgy enterprises. These are Novomet-Perm CJSC, Kamkabel OJSC, Novomet-Service LLC, Perm Research and Production Instrument-Making Company OJSC, Metallurgical, Morion OJSC, as well as defense enterprises.
The electric power industry is represented by Territorial Generating Company No. 9, created as a result of the reform of the energy industry. There are four thermal power plants and the Kamskaya hydroelectric power station in Perm.
KamHPP. Photo by V.M. Korovin
The main enterprises in the oil and gas refining sector are the offices of subsidiaries and Permregiongaz. The petrochemical industry is represented by Kamtex-Khimprom OJSC, Mineral Fertilizers OJSC, SIBUR-Khimprom CJSC and other enterprises located in Perm that produce fertilizers, paints and varnishes and detergents.
Over 60% of the region's area is covered by forests, 70% consisting of coniferous species, the most economically in demand. Forest resources make the Perm region one of the leading bases of the timber industry. In the field of woodworking, the leaders are OJSC Perm House-Building Plant, OJSC Lumber Red October, LLC Perm Cardboard. The largest printing enterprise of national importance is the Perm Goznak factory.
The food industry is represented by dozens of enterprises, the leaders are the Perm dairy and meat processing plants, confectionery factories - “Permskaya” and a branch of Nestlé Russia.
A striking feature of the city is its developed network of design organizations, research institutes, and universities. Research institutes and design and implementation organizations are engaged in conducting comprehensive research, studying rocks, oil, water, gases, designing and creating new technologies, materials and structures. The largest ones include the Scientific Center for Powder Materials Science, the Galurgy Research and Design Institute, the Ural Research Institute of Composite Materials, and regional branches of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The largest educational and production base in the region is Perm State University, established in 1916, which today actively cooperates with European and American educational centers.
Business and service enterprises are represented by a large number of organizations. The leading ones among them are large shopping, office and entertainment centers located in different regions of the city, although the largest number of them are located in the center of Perm. The central department store is located at the bus and trolleybus stop of the same name (the intersection of Lenin Street with Komsomolsky Prospekt) in an old but completely restored four-story building; there is a McDonald's on the ground floor.
Not far from it, in modern multi-storey buildings, there are multi-profile shopping and entertainment complexes “Almaz” and “Colosseum” with their own parking lots, with representative offices of famous brand companies, cinemas and restaurants.
Business center of Perm
Hypermarkets and multi-profile shopping centers Castorama (Castorama), METRO Cash & Carry, Capital are located in the Industrial district of the city, in modern buildings, equipped with parking lots.
According to the city statistics department, the standard of living of the population is determined this year by the following figures. The average monthly salary of employees of organizations with more than 15 people (not related to small businesses) in May 2012 amounted to 28,780.5 rubles and compared to the same period in 2011 increased by 17.8%.
The leaders in wages among the city's enterprises were the following industries: "Mining" - 52800.0 rubles, "Financial activities" - 51895.1 rubles, "Petroleum products production" - 46185.1 rubles, the "Pulp" industry closes the list -paper production, publishing and printing” – 33091.7 rubles. Workers in the education sector received an average of 19,257.8 rubles, healthcare workers - 21,439.1 rubles.
The city's attractions
Previously, we already figured out how old the city of Perm is, what this settlement is known for, and also got acquainted with its history. The city has many attractions that definitely need to be talked about. Most often in Perm you can find various architectural monuments. The Meshkov House is of great interest. This is a wonderful example of the style of Russian classicism. It is impossible not to pay attention to another remarkable building - the Gribushin House. It was created a little later, the construction was made in the Art Nouveau style.
Like many other cities, Perm has a monument to V.I. Lenin. It has a special status and is included in the list of objects of federal significance. The monument was opened in 1955. There are also relatively new monuments in the city. For example, in 2006, the stone monument “The Legend of the Perm Bear” was inaugurated here. The sculpture received great fame and wide publicity. Subsequently, it was replaced with bronze and moved to another place.
Once in Perm, you should definitely explore such wonderful places as the Bishop's House, the Transfiguration Cathedral and much more.
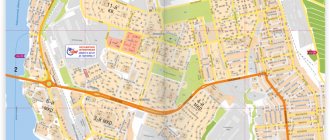
Districts and real estate of Perm
City map. Districts of Perm
The city-forming axis of Perm is the Kama River; the city itself is divided into left-bank and right-bank parts. The historical and now modern administrative, business and cultural center of the city is located on the left bank of the river. There are also architectural monuments, cultural centers and museums, cathedrals and temples.
The wide, flat space of the left bank of Perm has a regular layout, wide squares and central thoroughfares. Almost half of the city's territory is occupied by urban forests and recreation parks.
There are seven large urban districts in Perm: Leninsky, Ordzhonikidze, Dzerzhinsky, Kirovsky, Industrialny, Sverdlovsky and Motovilikha.
The most popular residential areas for living are located in the Leninsky, Sverdlovsky, Motovilikha and Dzerzhinsky districts of the city.
Leninsky district
The smallest central district of Perm in terms of area and most significant in terms of cultural, scientific and business potential. Leninsky district is located in the historical center of the old city on both banks of the Kama River, occupying 47.5 square meters. km. From north to south, the territory of the district stretches for 6 km. The main part of the region is southern, left bank. An important transport hub is located here – the River Station.
The population of the district is 48.5 thousand people. Representative offices of government agencies, educational, scientific and cultural institutions, and industrial enterprises are located in seven microdistricts.
The region has more than 10 thousand different enterprises, the largest representing the fuel and energy complex, mechanical engineering and food industry: LLC LUKOIL-Permneft, Russian Railways branch Permsky MRZ, Perm Telephone, Permavtodor, First Bread. On the territory of the district there is a central market, the main post office, Central Department Store, and large shopping and entertainment complexes. The transport network is well developed. Healthcare is represented by central city and regional hospitals and clinics.
Leninsky district ranks first in the number of higher educational institutions. Pharmaceutical, medical and agricultural academies, institutes of arts and culture, railway transport, a technical university, a branch of the Russian Academy of Painting, Sculpture and Architecture provide applicants with a wide choice of future professions.
Opera and Ballet Theatre. Permian
Leninsky district is also the center of cultural life in Perm. There are museums and libraries, exhibition halls and galleries, a philharmonic society, and theaters here. Here, lovers of classical and contemporary art can visit exhibitions, performances and art projects of international level.
As you may have guessed, the Leninsky district is the most prestigious area of the city, as evidenced by the highest real estate prices. True, we must remember that we are talking about the left bank part of it. The most expensive multi-storey construction, a small sector of cottage houses, luxury new buildings - for the right price.
New building in Leninsky district
Real estate prices in the historical, cultural and business center of Perm are expected to be the highest in the city. The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Leninsky district is 59.35 TR/sq.m, on the secondary market - 56.97 TR/sq.m.
Ordzhonikidze district
It occupies 22% of the city's territory, located on both banks of the Kama. The area is 178.5 km2, of which about 40 km2 is built up, which is 22% of the entire territory. Area of private residential development, garden plots and industrial enterprises.
The Ordzhonikidze district is largely an industrial sector of the city and an area of predominantly private residential sector, which makes up a quarter of all development. The population is about 113 thousand people living in 11 microdistricts. At the same time, the Chusovoy microdistrict is located 30 km from the city center, and the Malye Reki microdistrict consists of three cottage villages.
The industry is represented by large enterprises: Kamskaya HPP, NPO Iskra, Uralhydrostal, Kamkabel. Despite the large industrial areas, the area is quite “green”, there are park areas and recreation areas, and there are over a hundred gardening associations located here.
The infrastructure of the district includes educational institutions - kindergartens, schools, gymnasiums, lyceums, art schools; medicine – clinics and inpatient treatment units; culture and sports. There are three sports schools, halls, two stadiums – “Gaiva” and “Molniya”, two yacht clubs.
The housing stock of the Ordzhonikidze district as of March 1, 2012 is 4,355 houses. Among them are 850 apartment buildings and 3,505 private houses. In 2011, 8 high-rise buildings were put into operation.
Ordzhonikidze district of Perm
It should be noted that the distance from the city center and difficulties with transport links in the Ordzhonikidze district microdistricts are not a priority when purchasing housing. In this regard, real estate prices here are more affordable than in other areas of the city. The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Ordzhonikidze district is 33.54 TR/sq.m, on the secondary market - 38.74 TR/sq.m.
House on Chernyakhovskogo, 49
Dzerzhinsky district
The area of the district is 64.2 square meters. m., population about 150 thousand people. The area is rightfully considered the transport gateway of Perm; the Perm-2 and Perm-Sortirovochnaya railway stations, the Port of Perm and the Zaostrovsky cargo terminal are located here. At the same time, the Dzerzhinsky district is the center of the city’s scientific life; it is here that Perm State University is located. The city-forming enterprise of the district is the Machine-Building Plant named after. F.E. Dzerzhinsky.
Permian. Dzerzhinsky district
The area is actively under construction, with a large number of modern high-rise buildings, developed infrastructure and a good transport network. There are many park areas equipped for recreation, a large territory of the Chernyaevsky forest. Qualified medical care is provided by clinics and hospitals, educational services are provided by kindergartens, schools, lyceums, technical schools, colleges and universities.
The most prestigious in terms of real estate are the Center 2 microdistricts with elite multi-storey buildings, Parkovy, Svetly and Danilikha. The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Dzerzhinsky district is 46.69 TR/sq.m, on the secondary market – 52.01 TR/sq.m.
Industrial district
The third largest population - about 160 thousand people live here - the Perm region occupies almost 10% of its area: 69 sq. km. Two airports - Barakharevsky for local airlines and Bolshoye Savino, which operates international flights, make the area the “air gateway” of the city.
Already in the name of the district one can feel the power of large industrial enterprises located in the south-eastern part: OJSC Mineral Fertilizers, LLC Lukoil, CJSC Sibur-Khimprom, LLC Spetsneftetrans.
13 microdistricts are located on the left bank of Perm and do not have access to the Kama. One of the small city rivers, Mulyanka, flows through the area. A large green area is represented by the Chernyaevsky Forest recreation park. A popular recreation spot is the city hippodrome.
Good transport links are provided by the central highways of Mira and Sviyazeva streets, Kosmonavtov Highway, Dekabristov Avenue.
For purchasing real estate, the most convenient and popular neighborhoods are those located closer to the city center: Balatovo, Eranichi, Nagorny. The construction of multi-apartment residential buildings is actively underway here. Thus, in July 2012, a residential building with 127 apartments with a total area of 6,190.10 square meters was put into operation. m on Ippodromnaya street. The construction was carried out within the framework of the “People's Apartment” program with the improvement of the adjacent territory and the established infrastructure.
The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Industrial District is 44.2 rubles/sq.m, on the secondary market – 51.42 rubles/sq.m.
Kirovsky district
The greenest of the city's districts, its area of 156 sq. km is three-quarters occupied by urban forests and forest parks. The population is about 150 thousand people living in 10 microdistricts. There are 16 chemical and mechanical engineering enterprises in the area, including Perm Powder Plant and Sudo.
Medical care is provided by several adult and children's hospitals and clinics. Education is mainly represented by preschool and secondary general education institutions, and several sports schools. The district is decorated with architectural monuments of the 19th century and the specially protected natural area Sosnovy Bor.
Residential real estate in the Kirovsky district is not particularly popular due to its distance from the center and significant problems with transport links with other urban areas. But housing prices here are much more affordable. The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Kirovsky district is 37.10 rubles/sq.m., on the secondary market – 42.92 rubles/sq.m.
Motovilikha district
A large district of Perm, covering an area of 171.5 square meters. km and includes 17 microdistricts with a population of about 180 thousand people. A special feature of the area is the close interweaving of urbanized urban development with large green forests. The private residential development sector is significant here, but since the mid-1990s, the formation of blocks of modern multi-apartment buildings has begun.
Here is the main city-forming enterprise of Perm - OJSC Motovilikha Plants, a developer and manufacturer of weapons systems, tracked and automotive special equipment, and various equipment. The area is becoming another center of not only industrial, but also cultural life of the city. There are a circus, a planetarium, and museums here.
The infrastructure is represented by healthcare institutions - hospitals, clinics, education - institutes, colleges, schools, about 30 schools and more than 30 preschool institutions.
Some Motovilikha microdistricts occupy leading positions in the popularity rating of residential real estate in Perm. In 2000, construction began on the new Iva microdistrict. The Gorki microdistrict, although located closer to the city center, is inferior to new buildings in the quality of housing; there are mainly Soviet “Khrushchev” buildings here. The greatest demand is for residential real estate in the Sadovyi microdistrict, which is being actively developed with new multi-apartment buildings. The remaining microdistricts of Motovilikha are much inferior in the real estate category.
Permian. Microdistrict Sadovy
The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Motovilikha district is 44.52 t.r./sq.m., on the secondary market – 51.03 t.r./sq.m.
Sverdlovsk district
The largest district of Perm, Sverdlovsky occupies an area of 122.34 square meters. km and consists of 13 microdistricts. More than 200 thousand people live in it. Unlike other areas of the city, there are no large green forests familiar to Perm residents; almost the entire territory is inhabited. The city’s central thoroughfare, Komsomolsky Prospekt, or Kompros, runs here, dividing the area into western and eastern sides.
Permian. Sverdlovsk region. Photo by V. E. Zarovnyannykh
A popular area for those wishing to purchase an apartment. More than 1,200 houses with a total area of 3.6 million square meters are in unprecedented demand among Perm residents. Here you can choose suitable housing both in elite high-rise buildings and in apartment buildings built according to improved Soviet designs, buildings with economy-class apartments and spacious apartments in new buildings. The most prestigious microdistricts are Center, Sverdlov, Gromov and Ostrovsky. The outskirts of the Sverdlovsk region are already experiencing all the “delights” of being remote from the center - lack of public transport and traffic jams, failures of utility lines.
The main industrial enterprise of the region remains JSC Perm Motors; enterprises of the mechanical engineering, aviation and food industries are widely represented. Numerous healthcare institutions, the city's leading universities and numerous cultural centers and monuments make the area the real heart of a huge city. Well, fans do not miss a single match of their favorite Amkar team, held at the Zvezda stadium.
The striking attractions of the area are the central garden named after. M.I. Gorky with a rotunda built in 1842, the Spaso-Preobrazhensky Cathedral and the monument to Nicholas the Wonderworker above the Kama embankment. It was at the feet of Nikolai Ugodnik that the infamous “crazy bus” slowed down in 2009.
Cathedral and monument to Nicholas the Wonderworker
The supply price for apartments on the primary market in the Sverdlovsk region is 51.45 t.r./sq.m., on the secondary market – 52.33 t.r./sq.m.
Interesting facts about the city
Of course, due to its rich history, Perm is surrounded by a lot of interesting facts. General information about the locality, attractions and much more has already been sorted out. We also learned about how many years the city of Perm has already existed, when the city day is celebrated. It’s definitely worth telling a few interesting facts about this city.
In 1842, a big fire started in the city, as a result of which the entire central part of the city was destroyed. It is also known that there was a flood here in 1914. The Kama River overflowed and flooded several settlements at once. The water level in it rose by as much as 11 meters. Particularly interesting is the fact that the first Soviet stamps were issued in Perm.
Crime
In the ranking of the crime level in Russia, conducted by RIA-Analytika experts, the Perm Territory ranks 10th. These positions in the region have been maintained over the past ten years. About half of the registered crimes in Perm in 2011 and the first half of 2012 were thefts. In 2012, 3.4 thousand grave and especially grave crimes were registered (26% of the total), the detection rate was 56%.
Police Colonel P.V. Fadeev, head of the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs for Perm, assessing the general crime situation in the city, the number of “domestic” murders and grievous bodily harm due to alcohol intoxication is growing.
Perhaps the most large-scale crime of recent years in Perm was the famous “robbery of the century,” committed in 2009 by collector Alexander Shurman, who stole 250 million rubles right at his workplace. In terms of the value of the stolen goods, the absence of victims, and the speed of detection, this robbery surpasses the previous high-profile case of a bank car robbery in 2007, when the criminals injured two security guards during the attack, stole 5 million rubles and were detained a few months later.
Despite threats to former fellow collectors with firearms, no one was hurt at the hands of Schurman. The criminal hid in the forests for a week until he was discovered by special forces during Operation Interception.
Biography of Vasily Tatishchev
The biography of Vasily Tatishchev is typical for contemporaries of Peter I. He was born in 1686 near the city of Pskov, on the estate of his father, Nikita Alekseevich Tatishchev. Nikita Alekseevich served in Pskov, which at that time was a border city and a major trading center. From 1693 to 1696 Vasily Tatishchev was in Moscow, at the court of Tsar Ivan Alekseevich, co-ruler of Peter. Vasily Tatishchev entered the army in 1706, with the rank of lieutenant.
From 1706 to 1711, Vasily Tatishchev took part in hostilities with the Swedes. In the battle of Poltava he was wounded, and in 1711 he took part in Peter’s notorious campaign on the Prut River. After the Prut campaign, Vasily Tatishchev was sent to study in Europe. He spent abroad (with interruptions) from 1712 to 1716. In 1714, Vasily Tatishchev married Avdotya Andreeva, the daughter of a nobleman. In 1716 he received the rank of engineer lieutenant from the artillery, and from that moment his service under Peter I began.
The biography of Vasily Tatishchev is inextricably linked with Peter I. Since the beginning of his service under the sovereign, Vasily Nikitich has been improving artillery and cannons, as well as bringing it to the level of artillery in leading European countries. In addition to artillery, Tatishchev was engaged in diplomatic work, organizing a meeting of the Swedish and Russian delegations on the Åland Islands in 1718, but the peace negotiations were unsuccessful.
Portrait of Tatishchev
In 1720 there comes a key moment in the biography of Vasily Tatishchev. He receives a direction to the Urals to establish state-owned plants for smelting copper and silver ore. By royal decree, Vasily Tatishchev was ordered to look for ores near Kungur (where there was already a copper smelter), but a copper smelter near the Iset River was recognized as more promising. There, a mining office was founded, which was in charge of state-owned factories. Vasily Nikitich worked for the first time in the Urals from 1720 to 1723. In 1722, following Demidov’s denunciation, he was removed from the post of mining chief and recalled to St. Petersburg.
After two years of proceedings, Vasily Tatishchev was acquitted and assigned to diplomatic work in Stockholm. Carrying out government orders, Vasily Tatishchev gets acquainted with Swedish ironworks, which in the first half of the 18th century were the most advanced in the world. Also, Vasily Nikitich gets acquainted with the general organizations of the mining industry, the study of which, in the future, made it possible to create a mechanism that works like a clock in the Urals.
Silver medal with Vasily Tatishchev, in honor of the founding of the city of Yekaterinburg.
Since 1727, Vasily Tatishchev has held various court positions. From him came the initiative to reform the monetary circulation of Russia, which resulted in the streamlining of the monetary system. In particular, on the initiative of Vasily Tatishchev, the minting of small copper coins was resumed - money (half a penny) and half a penny (quarter of a penny) with an increase in the coin foot. From 1 pound of copper they began to mint coins worth 10 rubles, which was 4 times less than under Peter I. This significantly improved the state of the monetary system, which was in a difficult situation after the Northern War.
In 1731, Vasily Tatishev fell out of favor with the all-powerful favorite Biron, who did not like the vigorous activity of the intelligent courtier. Tatishchev is put on trial for embezzlement, but they could not prove Vasily Nikitich’s guilt. Being under investigation for three years, only in 1734 Tatishchev received his freedom and was again appointed as a mining chief in the Urals. With his arrival in the Urals, Tatishchev abolished the Oberbergamt, which was in charge of all factories in the Urals, and instead created the office of the main board of the Siberian and Kazan factories. Bergamts began to be called mining authorities, in addition to them various offices and the treasury were formed.
Vasily Tatishchev’s personal star on the Walk of Fame in Perm
Having reorganized the mining management in the Urals, Vasily Tatishchev energetically began building new factories. During his tenure as mining chief, 10 large plants were founded, among which were: Motovilikha, Sylvensky, Nizhne-Yugovsky, Revdinsky and Utkinsky plants. Contemporaries note Tatishchev’s toughness and integrity during this period; even the all-powerful Akinfiy Demidov was afraid of him. In 1737, Vasily Nikitich was appointed head of the Orenburg expedition, which he led until 1739.
Stamp with Vasily Tatishchev, issued in 1991
Returning to St. Petersburg in 1739, Vasily Tatishchev again found himself on trial. This time, for embezzlement, he is imprisoned in the Peter and Paul Fortress, where he spends more than a year. The coming to power of Empress Elizaveta Petrovna was marked by the release of Tatishchev and his appointment to the post of governor of Astrakhan. This appointment, which was not suitable for such an active person as Vasily Nikitich, became the last in his track record. In 1745, he retired and retired to his family estate Boldino, where he lived until his death in 1750.
The biography of Vasily Tatishchev is an example of the ups and downs of a talented scientist, diplomat, statesman and organizer. Through his service to the Fatherland, he made a significant contribution to the development of the country's industry. During his 40 years of service to the country, Vasily Nikitich managed to organize a new type of industry in the Urals, which later became one of the key factors in Russia’s victories in the international arena. Intelligence, foresight and the ability to foresee the further development of the situation - all this puts him among the ranks of outstanding figures of the 18th century.