Novosibirsk is the administrative center of the Novosibirsk region, the unofficial capital of Siberia, the official center of the Siberian Federal District (Siberian Federal District) and the municipal formation of the Novosibirsk region. The key city of “Big Novosibirsk”, the Novosibirsk agglomeration, which also includes the cities of Ob, Iskitim, Berdsk and the villages of Koltsovo and Krasnoobsk.
Novosibirsk is located on the right and left banks of one of the largest rivers of the Russian Federation - the Ob, on the Priobsky plateau in the south-eastern part of Western Siberia, near the Novosibirsk reservoir, Kudryashovsky and Zaeltsovsky forests, at a distance of 3191 km from Moscow.
The city is the third most populous in Russia and ranks twelfth in area with an area of 502.7 km².
On September 23, 1983, Novosibirsk was awarded the Order of Lenin.
History of Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is a young and rapidly developing city. Its history is an amazing combination of events that intertwined into a single mosaic, which led to the birth of one of the symbols of the greatness of Russia. The beginning was made in 1891, when Emperor Alexander III issued a decree on the start of construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway (original name - Siberian Road), which was supposed to connect Chelyabinsk (Southern Urals) and Vladivostok (Far East).
In 1893, one of the great and legendary people of that time, Minister of Finance Sergei Yulievich Witte, proved the feasibility of building a railway bridge across the Ob River in the area of the village of Krivoshchekovo, where the ruins of the Teleut fortress were located on the right bank. No sooner said than done, on April 30, 1893, engineer G.M. arrived from Kolyvan. Budagov, and the construction of engineering structures and a workers’ camp for bridge builders began. This is how Novosibirsk was born.
Initially, the village was named Aleksandrovsk in honor of the emperor, but four years later (02/17/1898) it was renamed Novonikolaevsk (Novo-Nikolaevsk) in honor of the last emperor Nicholas II. Novosibirsk received its modern name on February 12, 1926.
Main historical milestones of the city:
- On December 28, 1903, by rescript No. 747-47, signed by Emperor Nicholas II, it acquired the status of a city without a district;
- 12/11/1908 – awarded the status of a full-fledged urban settlement;
- 04/17/1917 - becomes a district and becomes part of the Tomsk province (it could have become a provincial center, the center of the Altai province in 1916, but it did not work out);
- 12/23/1919 - became the provincial center of the Tomsk province;
- 13.06. 1921 – acquired the status of a provincial city in the Novonikolaevsk province;
- 05.25.1925 – after the formation of the Siberian Territory, it was given the status of an administrative center;
- 07/30/1930 - as a result of territorial and administrative reform, it was transformed into the center of the West Siberian Territory;
- 09.28.1937 – acquired the status of a regional center of the newly formed Novosibirsk region;
- 08/21/1943 – withdrawn from regional subordination and becomes a separate administrative structural unit under republican subordination;
- 07/03/1958 – return to regional subordination with the status of a regional center;
- 09/02/1962 – 70 years after its founding, it becomes the youngest city in the world with a million population;
- 05/13/2000 - by presidential decree, it was given the status of an administrative center of the Siberian Federal District (Siberian Federal District).
The intensive development of Novosibirsk was associated with its favorable geographical location, the intersection of water transport routes (the Ob is a navigable river) and the Trans-Siberian Railway. This ensured the rapid growth of trade, banking and industry.
During the Soviet years, this trend intensified largely due to industrialization and the city’s status as the center of the Siberian region, which made it possible to concentrate significant financial and economic resources in Novosibirsk. The impetus for the development of the city was the Great Patriotic War. In the post-war period, Novosibirsk became one of the largest scientific centers in the country, and industry acquired a distinct defense specificity.
In the 90s of the last century, industrial production focused on the defense industry collapsed and decreased at a precipitous rate. Now Novosibirsk is developing dynamically, has turned into a large trade and financial center and has managed to maintain its scientific base in difficult years, which allows us to look into the future with hope.
Temples
The main temple of the city is the Ascension Cathedral, which was built in 1913. This was the first wooden temple in the city. Today, services are held daily in the Ascension Cathedral, which every believer can attend.
One of the oldest cathedrals in Novosibirsk is the Alexander Nevsky Temple. Emperor Nicholas II provided assistance in the construction of the temple; it was he who allocated a plot of land for the construction of the temple.
Climate of Novosibirsk
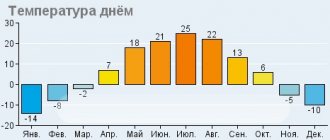
The climate of Novosibirsk is distinctly continental, with characteristic significant differences (jumps) in temperatures within 38°C, which is very significant. Therefore, the comfort of living in the city is low. The picture is complemented and aggravated by squally winds, which are not uncommon in these places.
Main climatic characteristics:
- air temperature (average annual) + 1.8 ° C;
- average temperature in July +19 ° C;
- the average temperature in January is 16 ° C;
- historical minimum temperatures -51.1 °C (January 1915);
- historical maximum temperature + 40.8 ° C (07/12/2014);
- average annual precipitation – 400 mm;
- the winter period lasts 5-6 months (winter can last up to 165 days, very severe and long, with squally winds, snowstorms and stable snow cover);
- the summer period lasts 2-3 months (summer is short, on average 87 days, hot, begins at the end of May and ends at the end of August);
- transition periods spring and autumn are very short and characterized by very unstable weather;
- average wind speed – 4 m/s.
In general, compared to the climatic conditions of the settlements of the American continent located in these latitudes, the climate of Novosibirsk is less severe, but not for sissies.
Ecology of Novosibirsk
The ecology in the city is ambiguous. On the one hand, natural forests have been preserved in Novosibirsk itself and its suburbs, plus such recreational resources as the Ob reservoir, the Ob, and many small rivers and lakes. On the other hand, the city is a large industrial center with a developed chemical industry, a metropolis with about 1.5 million inhabitants, which negatively affects the environmental situation.
Air pollution in the city is associated with factors such as:
- road transport (66%);
- thermal power plants (25%);
- industrial enterprises (4.5%);
- boiler rooms (4%);
- individual heating.
Emissions into the atmosphere amount to 300 – 360 thousand tons per year.
The main pollutants are:
- formaldehyde (from 3 to 4.6 MAC);
- benzopyrene (up to 3.1 maximum permissible concentration);
- nitrogen dioxide (from 1.2 to 1.5 MPC);
- ammonia (up to 1.3 MPC);
- hydrogen fluoride (up to 1.2 MPC);
- dust (up to 1.3 MAC).
Soil pollution is associated with two factors:
- radiation situation;
- waste generation.
Within the city there are several enterprises and institutes of the nuclear industry, so in some areas (there are about 217 of them) the background radiation significantly exceeds the maximum permissible standards. Although most of these facilities are no longer functioning. The most difficult situation is in the Kalininsky region, at the chemical concentrates plant (the presence of such carcinogenic substances as methylene chloride, benzene and carbon tetrachloride was discovered in the atmosphere there).
The situation is aggravated by the fact that 8 out of 10 districts of the city are located on a granite massif with a high content of uranium-238 and radon-222, which increases the level of natural radiation and can lead to serious diseases.
The volume of solid household waste is 2 million cubic meters, industrial waste - 500 thousand tons. Moreover, some of the waste ends up in unorganized landfills (there are about 170 of them in Novosibirsk, with a total area of 14 hectares), located on the banks of rivers and ravines, which significantly worsens the environmental situation in the city.
The situation with water resources is also difficult. The Ob Reservoir receives contaminated water from other regions. Surface flow is 65 million cubic meters per year, which is why the following flows into the main water artery of the region:
- suspended substances (27 thousand tons per year);
- petroleum products (1.2 thousand tons);
- floating substances (1 thousand tons, including biogenic, organic substances and chemical compounds).
It should be taken into account that the main water intake to meet the drinking water needs of the population is taken from the Ob River. In general, thanks to significant financial resources and targeted programs, the environmental situation in Novosibirsk is improving every year, as evidenced by the fact that the city is already in 50th place in the environmental development rating of Russian cities, and is not at the bottom of the list.
Population of Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is a unique, third largest city in the Russian Federation, from a working-class village in 100 years it has turned into a metropolis with a population of one and a half million. It was one of the fastest growing cities in the world, which is reflected and recorded in the Guinness Book. The population of the city as of January 1, 2019 is 1,618,039 thousand inhabitants. This is 70 thousand more than in 2014.
The population density of Novosibirsk is about 3 thousand people per 1 km2. Population growth dynamics are positive, which is due to:
- a decrease in mortality compared to birth rates (18,383 people versus 20,792 babies);
- pendulum migration.
Natural increase – 2409 people (14th place among cities of the Russian Federation).
The natural increase rate is 1.5%. Migration exists:
- intraregional, due to the influx of rural population to the regional center;
- international (thanks to the favorable geographical location and powerful economic development of the region, a large influx of labor migrants, including illegal ones, has emerged from the CIS countries, Central and Southeast Asia, China, Kazakhstan, Ukraine).
- In 2022, population growth amounted to 6 thousand people
The population structure is as follows:
- working population more than 64% (965,616 people, largely thanks to labor migrants);
- children – 14% (230,678 people);
- pensioners – 22% (351,616 people).
As in many other regions of the Russian Federation, the female population of Novosibirsk predominates over the male population. The ratio is 835,570 to 712,190 citizens, or a percentage of 55% to 45%.
The number of marriages exceeds the number of divorces, 14,627 versus 7,910; according to these indicators, Novosibirsk confidently ranks 3rd in the Russian Federation. About 75% of marriages break up, but many spouses re-create families after realizing their mistakes. The main age category of those getting married is 20-34 years old, there is a trend towards aging marriages; just a few years ago the age category was 18-24 years old.
The national composition is homogeneous. The majority of the population (1,269,979 people or 92.82% of the total population of the city) are Russians. Other nationalities are represented insignificantly and occupy no more than 1% in the structure of the national composition of the metropolis. The most represented are Ukrainians, Tatars, Germans, Tajiks and Uzbeks. A significant difference is observed in the ratio of men and women by nationality. Thus, among Russian Novosibirsk residents there are 81 men per 100 women, and among the Chinese living in the city, this ratio is 100 to 640, and for Turks 100 to 2060.
In general, the demographic situation in Novosibirsk is stable, with positive dynamics.
Famous people of Novosibirsk
The founder of the city is Nikolai Georgievich Garin-Mikhailovsky, heir to an ancient noble family. It was he who insisted that the Trans-Siberian Bridge on the Ob be built near the village of Krivoshchekovo (the village was named after Fyodor Krenitsyn, a Tomsk serviceman who received the nickname Krivoshchek for the ugly saber scar on his face).
In the original plans, the construction of the bridge was planned near the village of Kolyvan. If this had happened, then there would be no modern Novosibirsk, but maybe there would be Novokolyvanovsk. Nikolai Georgievich was the godfather of Emperor Nicholas I and had influence at court. And besides this, Nikolai Georgievich is a widely known Russian writer.
Yuri Vasilyevich Kondratyuk is one of the legendary Russian theorists who developed the concept of interplanetary travel and the pioneer of Russian cosmonautics. The Americans used his developments when landing their modules on the Moon.
He settled in the city in 1927, where in 1929 he wrote the work “The Conquest of Interplanetary Spaces,” and he also wrote the work “For Those Who Will Read to Build,” where he outlined the design features of a four-stage rocket. These developments were 30-40 years ahead of their time, and it is a pity that the domestic cosmonautics was able to bring them to life and only partially implement them.
Alexander Ivanovich Pokryshkin is a legendary ace of the Great Patriotic War, who terrified the seasoned Luftwaffe aces. 59 aircraft shot down, 600 sorties, 156 battles fought, three stars of the Hero of the Soviet Union. Novosibirsk residents are rightfully proud of such a fellow countryman, having named a street and a metro station in honor of Alexander Ivanovich.
Novosibirsk has become one of the key scientific centers of Russia thanks to the great scientists who worked in the city:
- Chaplygin Sergei Alekseevich – the founder of such sciences as aerodynamics and hydrodynamics;
- Leonid Vitalievich Kantorovich - Nobel laureate in economics;
- Mikhail Alekseevich Lavrentyev, the founder of scientific centers located in Siberia, who headed the Siberian branch of the USSR Academy of Sciences.
Alexander Sergeevich Zatsepin, who is a native Novosibirsk resident, is a composer who wrote music for such legendary films as “Operation Y and other adventures of Shurik”, “The Diamond Arm”, “Ivan Vasilyevich changes his profession”. In particular, folk hits such as “Song about Hares”, “Conversation with Happiness”, “There is only a moment”.
Novosibirsk is the birthplace of many famous singers, athletes and scientists, about whom you could write a book in several volumes, because the Novosibirsk land is rich in its talents.
Automobile highways
Six main highways pass through Novosibirsk:
- Federal highway P254 to Omsk.
- Highway P255 to Tomsk, Kemerovo and Krasnoyarsk (federal highway "Siberia").
- Route 50K12 of regional significance to Kolyvan, Tomsk and Kolpashevo.
- Federal highway P256 (Chuysky tract) to Barnaul, Biysk and Gorno-Altaisk.
- Highway P380 of regional importance to Ordynsky, Kamen on the Ob and Pavlodar.
There are three bridges across the Ob River - Bugrinsky, Oktyabrsky and Dimitrovsky. These are the most picturesque sections of roads within the city.
Economy of the city and region
The economy of the Novosibirsk region is characterized by positive development dynamics, which is due to a high degree of diversification, the formation of a favorable business climate, infrastructure development and increased business activity.
The industrial production index for the previous year 2013 compared to 2012 was 102.20%. Enterprises of the extractive industry developed most dynamically, the growth of the production index was 119.5%. Industrial production index of manufacturing industries – 101.8%.
The high level of diversification of the economy of the Novosibirsk region is ensured by the wide representation of various sectors of the national economy, including the following:
- Agriculture;
- construction;
- industrial production;
- transport and logistic;
- trade;
- connection.
The main potential for economic development of the Novosibirsk region lies in attracting investments, including foreign ones, and developing innovative, knowledge-intensive industries. The transport and logistics cluster is developing most intensively due to its favorable geographical location and the presence of a developed transport infrastructure, which includes:
- the West Siberian Railway with a length of 1,530 km, with the largest sorting station in Eurasia, Inskaya, and the Kleschikha container terminal;
- Tolmachevo international airport with a capacity of 1,800 passengers per hour on domestic flights and 750 passengers per hour on international flights, it can receive aircraft of any class;
- the navigable Ob River with ports and berths;
- federal highways P256 Chuisky tract (M 52, part of AN4 Novosibirsk - Karachi) and P258 Baikal (M54 Irkutsk - Chita, part of AN 6) and regional roads (the total length of roads in the region is 25,027 km, of which 820 km are federal roads, 12739 – regional roads, 9093 – local roads).
The construction cluster of the Novosibirsk region has recently shown high growth rates. There are about 370 enterprises (15 thousand employees) in the industry that produce building materials.
Moreover, for the production of building materials, local raw materials are used, including brick loams, sand, sand-gravel mixtures, limestones, agloporite and expanded clay raw materials, building stones, which makes it possible to produce cement, thermal insulation structures and materials, products from cellular concrete, glass, block- modular heating systems, a whole range of new inert wall materials based on the latest technologies. This, in turn, affects the pace of housing construction.
In terms of the pace of housing commissioning, the Novosibirsk region confidently occupies a leading position among all subjects of the Siberian Federal District.
In 2022, 1 million 60 thousand 239 meters of housing were commissioned. This is almost the same as in 2022 (1.050 million sq.m.) and 2022 (1.043 million sq.m.). Housing commissioning per person in the region amounted to 0.66 square meters. meters, which significantly exceeds the Russian average.
The maximum growth rate was in 2015, when 26,200 apartments with a total area of 1,742,600 square meters were commissioned. Then in 2107-2018 the decline began.
In the Novosibirsk region, significant attention is paid to the improvement of residential real estate. Share of urban living space equipped with:
- water supply – 88.9;
- sewerage – 86.1;
- central heating – 83.3%;
- baths – 79.1%;
- hot water supply – 75.9%.
High-tech and knowledge-intensive industries are also developing dynamically, the share of which in the total volume of gross regional product is 25.4%, compared with the Russian average of 19.7%.
It should be noted that an IT cluster has been formed in the Novosibirsk region (technopark Akademgorodok). Industries such as power electronics, electrical and power engineering, instrument making, as well as the biomedical technology industry are rapidly developing.
Mayor of Novosibirsk: Lokot Anatoly Evgenievich
Territory – 502.07 sq. km
Population – 1.625 million people
The city of Novosibirsk (until 1926 – Novonikolaevsk) was founded in 1893. Located in the southeastern part of the West Siberian Plain on the Priob Plateau, adjacent to the Ob River valley, next to the reservoir formed by the Novosibirsk Hydroelectric Power Station dam, at the intersection of forest and forest-steppe natural zones. The left bank part of the city has a flat topography, the right bank is characterized by many gullies, ridges and ravines, since here the transition to the mountainous terrain of the Salair Ridge begins. The city is adjacent to the Zaeltsovsky and Kudryashovsky forests and the Ob reservoir.
Novosibirsk has the status of a city district (the largest municipal entity in terms of population in the Russian Federation), and is the administrative center of the Novosibirsk region and the Siberian Federal District.
Novosibirsk is the third largest city in Russia by population (second only to Moscow and St. Petersburg) and the twelfth largest city in Russia. The permanent population as of January 1, 2022 is 1,625,631 people (58% of the population of the Novosibirsk region). Novosibirsk is included in the Guinness Book of Records as the fastest growing millionaire city. The number of its inhabitants reached 1 million in less than 70 years (the city's millionth resident was born on September 2, 1962). Chicago, with which Novosibirsk is often compared in terms of development rates, took 85 years for this, New York - 250, Tokyo - 400, Moscow - 700, Kyiv - 900.
Modern Novosibirsk is a business, trade, financial, scientific, industrial, transport, logistics and cultural center of the Asian part of Russia. In Novosibirsk there is the residence of the plenipotentiary representative of the President of the Russian Federation for the Siberian Federal District, a representative office of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation, the Siberian Customs Administration, representative offices of other federal bodies and departments, and the headquarters of interregional organizations are located.
The city is divided into eight administrative territories - Dzerzhinsky, Kirovsky, Kalininsky, Leninsky, Oktyabrsky, Pervomaisky, Sovetsky districts and the Central District. On January 1, 2013, the administrations of the Zheleznodorozhny, Zaeltsovsky and Central districts were reorganized in the form of their merger into a single Central District. The largest of them in terms of population is the Leninsky district - more than 300.0 thousand people (about 20% of the city’s population); by area - Sovetsky district (89.2 sq. km).
According to the results of the All-Russian Population Census of 2010, representatives of 180 nationalities and national groups were registered in Novosibirsk, while 89 of them had no more than 10 people. The absolute majority of the population is Russian - 92.8% of the population who indicated their nationality. The most numerous ethnic groups are Ukrainians, Uzbeks, Tatars, Germans, Tajiks, Armenians, Kyrgyz and other peoples.
Novosibirsk remains a center of attraction for migrants from Central Asia, the Caucasus, Siberia and Kazakhstan. In 2022, 45.5 thousand people arrived in Novosibirsk, the number of people who left the city was 37.1 thousand.
The revenue side of the budget of the city of Novosibirsk in 2022 was executed in the amount of 48.5 billion rubles, expenditures - 50.3 billion rubles, the budget deficit amounted to 1.8 billion rubles.
The main sectors of the city's economy are: industry, construction, transport, communications, trade and services (including the financial sector), science and scientific services. More than 95 thousand legal entities and 53 thousand individual entrepreneurs operate in the city.
The city’s economy employs about 810 thousand people, of which about 50% work in large and medium-sized enterprises and organizations of the city, more than 31% work in small enterprises (including micro-enterprises).
The basis of the city's industrial complex consists of more than 200 large and medium-sized industrial enterprises, which produce over 55% of the regional output of industrial products and services. The leading activities in the city's industrial production are manufacturing (76.7%) and the provision of electricity, gas and steam; air conditioning (19.9%). The largest share in manufacturing industries is in such activities as food production (14.6%), production of computers, electronic and optical products (14.2%), metallurgical production (13.2%), production of other vehicles and equipment (13.1%).
Novosibirsk is the largest transport hub in Siberia: the Trans-Siberian Railway, railways and highways pass through it, connecting Siberia, the Far East and Central Asia with the European regions of Russia. The administration of the West Siberian Railway is located in Novosibirsk. There are 4 railway stations in the city, of which the Novosibirsk-Glavny station is the largest beyond the Urals. Human and trade flows contribute greatly to the development of the city.
Novosibirsk is connected by air lines with more than 100 cities in Russia and the world. Within the city agglomeration there is one of the largest airports in the country and the largest in Siberia, Tolmachevo Airport, which has a Category II certificate according to the requirements of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and, due to its technical capabilities, can serve all types of modern domestic and foreign passenger aircraft. and cargo purposes. The presence of such a high-class airport provides a dynamic connection between the city and the largest metropolises of the world, which makes international business and tourist visits comfortable.
Two federal highways pass through Novosibirsk: M-51 “Baikal” (from Chelyabinsk via Omsk, Kemerovo, Krasnoyarsk to Chita with access to the federal highway “Amur” from Chita to Khabarovsk) and M-52 “Chuysky Trakt” (via Biysk to border with Mongolia).
Novosibirsk is also a river port. The intersection of water and land routes has become an additional factor in its growth. Navigation on the Ob consists of long-distance transportation of transit cargo, local passenger transport and sand mining.
Novosibirsk has demonstrated high rates of housing construction in recent years and is one of the leaders in Russia, providing the largest volumes of housing commissioning. In 2022, 1061.0 thousand square meters were commissioned. m of total area of residential buildings.
Trade occupies one of the leading places in the sectoral structure of the economy of the city of Novosibirsk. International retail chains operate successfully in the city; exhibitions are held at the largest international exhibition complex in Siberia, Novosibirsk Expo Center, which meets the best international standards and is currently one of the most modern in the country.
Novosibirsk is the scientific and educational center of Russia. Novosibirsk became famous worldwide thanks to the Novosibirsk Akademgorodok (Novosibirsk Scientific Center of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences), on whose territory dozens of research institutes and the Novosibirsk National Research State University (NSU) are located. Near the Academy Town there are institutes of the Department of Medical Sciences of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Not far from Novosibirsk, in the science city of Koltsovo, there is the State Scientific Center for Virology and Biotechnology “Vector”. The Siberian Federal Scientific Center for Agrobiotechnologies of the Russian Academy of Sciences (SFSC RAS) is located in the village of Krasnoobsk.
In Academgorodok there is Academpark, a comprehensive technology park with a unique scientific, technological and business infrastructure that allows creating the best conditions for the generation and development of innovative companies and the successful development of existing high-tech enterprises. Here scientific developments are translated into industrial technologies. Academpark is the largest science and technology park in Russia. The Academy Park is managed by OJSC Technopark of the Novosibirsk Akademgorodok.
The educational complex of the city of Novosibirsk is represented by an extensive network of preschool, general education, secondary and higher professional educational organizations, as well as the infrastructure of additional education. The city of Novosibirsk provides a high level of professional education; the maximum number of educational institutions of higher education in the Siberian Federal District that train specialists for all spheres of economic activity is concentrated here. The largest organization of higher education in the city of Novosibirsk, Novosibirsk National Research State University (NSU), improves its performance in world rankings year after year and is a participant in the National Technology Initiative.
On the territory of the city there are a number of regional, federal and departmental health care institutions, including the State Novosibirsk Regional Clinical Hospital, the regional clinical diagnostic center, the regional blood transfusion station, the Federal State Budgetary Institution Novosibirsk Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. Ya. L. Tsivyan (with clinic), FSBI Novosibirsk Research Institute of Circulatory Pathology named after. Academician E. N. Meshalkin, Novosibirsk branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution MNTK "Eye Microsurgery named after Academician S. N. Fedorov", Federal State Budgetary Institution "Federal Center of Neurosurgery" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Road Clinical Hospital at the "Novosibirsk-Glavny" station, Central Clinical Hospital of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and other.
Novosibirsk is a recognized cultural center of Russia. The attractions of Novosibirsk are theatres, among which the most famous are: the largest in the country, the Novosibirsk State Academic Opera and Ballet Theater (NOVAT) - a historical and architectural symbol and calling card not only of Novosibirsk, but also of Siberia and Russia as a whole, the academic theater "Red Torch" , academic youth theater "Globus", city drama theater under the direction of Sergei Afanasyev.
The leader of the city's musical life - the Novosibirsk State Philharmonic - unites about two dozen professional creative groups, among them well-known far beyond Russia: the Novosibirsk Academic Symphony Orchestra (founder - People's Artist of the USSR, Professor Arnold Katz); chamber choir; chamber orchestra; quartet "Filarmonica"; vocal ensemble of Pavel Sharomov; early music ensemble “Insula Magica”; choral ensemble "Markell's Voices", concert brass band, "Siberian Dixieland" and others.
Over the years of its existence, the Novosibirsk State Glinka Conservatory has trained several thousand musicians: performers, composers, musicologists, and today it is one of the leading conservatories in the country and is internationally famous.
The most important annual event in the cultural life of the city is the annual Trans-Siberian Art Festival, which takes place in Novosibirsk with the support of the Vadim Repin Foundation, a famous violinist, a native of Novosibirsk and a graduate of the Novosibirsk State Conservatory. The Trans-Siberian Art Festival is recognized as one of the most significant international forums in Russia.
The variety of cultural leisure of Novosibirsk residents is provided by a network of public libraries, including the largest in Siberia State Public Scientific and Technical Library of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, museums (Novosibirsk State Art Museum, Novosibirsk State Museum of Local Lore, Museum of Cossack Glory, Novosibirsk Museum of Railway Equipment named after. N.A. Akulinina, the Siberian Birch Bark Museum, the Roerich Museum N.K. and others), the largest children's and youth park in the Asian part of Russia, the largest indoor water park in Russia "Aquamir", cinema halls and cinemas with support for the latest multimedia technologies.
Novosibirsk Zoo named after R. A. Shilo is one of the largest zoos in Russia. It is located in a forested area, covering an area of 65 hectares. It houses more than 11 thousand individuals of almost 800 species of animals, of which several hundred species are listed in the International, Russian and regional Red Books. The zoo team, as part of the international unions EAZA, EARAZA and WAZA, maintains contacts with many zoos around the world and participates in international programs for the conservation of rare and endangered species of animals. The Novosibirsk Zoo has one of the world's richest collections of cats and mustelids; at a considerable distance from the seas and oceans, a unique project for Siberia was implemented for a high-tech, year-round stationary scientific and educational oceanographic complex - the Center for Oceanography and Marine Biology "Dolphinia".
Novosibirsk is rightfully considered a sports city. The city has 1,700 sports facilities, including a biathlon complex, the Siberia Sports Palace, 9 stadiums, 42 swimming pools, 28 ski lodges. About 600 thousand people are covered by physical education and health activities.
In 2022, the International Ice Hockey Federation approved the holding of the Youth World Hockey Championship in Novosibirsk in 2023. In this regard, a decision was made to build a new multifunctional ice arena in the Kirovsky district of Novosibirsk, which will facilitate the implementation of a number of important infrastructure projects in Novosibirsk.
The city of Novosibirsk has a developed tourist infrastructure, including modern accommodation and catering facilities. The following types of tourism are developed in the city: recreational (health), cultural and educational (excursion), business (business tourism, congress tourism), sports, medical, active (transport) tourism. The city of Novosibirsk provides over 80% of the total tourist flow of the Novosibirsk region.
Cooperation with sister cities is expanding. Currently, 14 cities are sister cities of Novosibirsk: Minneapolis and St. Paul (United States of America), Sapporo (Japan), Mianyang and Shenyang (People's Republic of China), Daejeon (Republic of Korea), Tiraspol (Transnistrian Moldavian Republic), Varna (Republic of Bulgaria), Osh (Kyrgyz Republic), Kharkov (Ukraine), Minsk (Republic of Belarus), Sevastopol (Russian Federation), Yerevan (Republic of Armenia), Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia).
Trade, economic, humanitarian and other ties between the city of Novosibirsk and countries near and far abroad are developing. Five consular offices of foreign states are accredited on the territory of the city of Novosibirsk: Consulate General of the Federal Republic of Germany, Consulate General of the Republic of Uzbekistan, Consulate General of the Republic of Tajikistan, Consulate of Ukraine, Consulate General of the Kyrgyz Republic. The honorary consuls of France, Croatia, Spain, Switzerland, and Austria are accredited and are active. There is a joint visa center that includes more than 20 countries (Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Spain, Canada, Lithuania, Malta, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Finland, France, Croatia, Czech Republic, Sweden, Estonia), UK visa center, Italy visa center. There are international organizations promoting trade exchanges and the development of cooperation in the fields of entrepreneurship and culture.
Investments
Novosibirsk and the Novosibirsk region are distinguished by a high degree of investment attractiveness. The region has been assigned a long-term national credit rating of AA+.
For the period from January to September 2014, the amount of investment in fixed capital amounted to 180.90 billion rubles, 12 investment projects with a total value of 58.22 billion rubles were accepted for implementation. In 2013, the amount of investment in the regional economy amounted to 174.60 billion rubles.
The volume of foreign investment is also increasing. In 2013, investors invested $859.50 million into projects, which is 111.4% compared to the same period in 2012.
Enterprises
Novosibirsk is one of the largest industrial centers in the Russian Federation. The city's industrial structure is widely differentiated and unique, not typical for most Russian cities. There are no city-forming enterprises, but there are many large and medium-sized factories and factories, of which there are about 214 in the city. They produce 2/3 of all industrial products of the Novosibirsk region. The average annual number of employees of all city enterprises is 421.2 thousand people.
The main sectors of the national economy represented in Novosibirsk:
- mechanical engineering;
- food industry;
- metallurgy;
- defense industry;
- electric power industry.
Largest enterprises:
- ELSIB (hydro-, turbogenerators, electric motors);
- NCCP (Novosibirsk Chemical Concentrates Plant produces fuel assemblies - nuclear fuel for nuclear power plants);
- metallurgical plant named after Kuzmin (wide range of rolled metal products);
- NAZ (V.P. Chkalov Aviation Plant, part of the Sukhoi corporation, produces Su-34 combat aircraft and parts for the civilian Superjet 100);
- Instrument-Making Plant (Russia's largest enterprise for the production of portable surveillance and reconnaissance systems);
- Noringa (the largest bottled water bottling enterprise in the CIS countries);
- Screen (the company is the largest manufacturer of glass containers in the region);
The electric power industry of Novosibirsk is represented by HPP, CHPP 5, CHPP 4, CHPP 3 and CHPP 2.
Airport
Novosibirsk Tolmachevo International Airport is the largest in Siberia in terms of passenger traffic (5.9 million passengers per year as of 2018). The airport has been awarded Platinum status by the International Air Transport Association IATA, which confirms 100% implementation of technologies to simplify airport formalities. Tolmachevo is also the 4th airport (after Domodedovo, Sheremetyevo and Pulkovo) to introduce 2D barcode encoding technology for boarding passes (BCBP).
Tolmachevo is a hub for three airlines - Russian S7 Airlines (main hub) and NordStar, as well as German Lufthansa Cargo (Lufthansa's cargo division). The air harbor not only serves civilian ships, but also military aircraft of the Russian Air Force are based (562 air base, covered from the ground by the 41st Air Defense Division).
Novosibirsk International Airport is located 17 km from the center of Novosibirsk on the outskirts of the city of Ob. There are buses and minibuses from the city to the air harbor, as well as regular trains running along the Trans-Siberian Railway; the nearest station is located 1 km from the airport.
From Tolmachevo Airport there are flights to many cities in the European and Asian parts of Russia. International flights operate to a large number of countries, including Germany, Spain, China, Vietnam, Thailand, Turkey, UAE, etc.
Cost of new buildings
The average cost per square meter of an apartment in new buildings in Nizhny Novgorod as of February 2022 is RUB 70,489.
The city as a whole consists of ten districts. Three of them (Zheleznodorozhny, Central and Zaeltsovsky) have been united into one district since the beginning of 2013. But, by and large, we can talk about three sectors. This is the right bank part (Zheleznodorozhny, Central, Zaeltsovsky, Kalininsky, Dzerzhinsky and Oktyabrsky), the left bank (Leninsky and Kirovsky) - and the Pervomaisky and Sovetsky districts, which stand somewhat apart (and Sovetsky, which includes the famous Akademgorodok, is located on both banks at once ).
The program for the resettlement of dilapidated and dilapidated housing in the city is quite tangible. This is explained not so much by the altruism of the authorities, but by the fact that the land occupied by this type of housing (especially closer to the center) is manna from heaven for developers. Therefore, the sharks of the construction business are developing such land very confidently.
Compared to other cities, Novosibirsk has a large number of developers. According to analysts, in the coming years the market will expand: local leaders are increasing their market share and the number of projects. The increase in housing starts observed in 2022 is largely due to the low base effect. The market is recovering from the serious decline of 2017-18. Plus, Novosibirsk has a significant supply of apartments at a high stage of readiness, more than 500 thousand sq.m., so an increase in housing commissioning is planned in 2022.
Developers who previously built intimate comfort-class residential complexes entered the mass market this year, becoming leaders in terms of commissioning rates. This made their marketing policy aggressive. Competition among residential complexes has ended in Novosibirsk. In one complex there are apartments of different types - an economy studio, a spacious three-room apartment and a high-flat apartment.
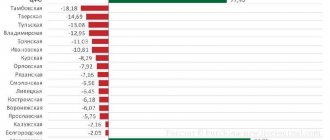
As of February 2022, average prices for apartments in new buildings in Novosibirsk are distributed by region as follows:
- Dzerzhinsky district – 72,804 rubles/sq.m;
- Zheleznodorozhny district – 88,326 rubles/sq.m;
- Zaeltsovsky district – 72,340 rubles/sq.m.;
- Kalininsky district – 70,708 rubles/sq.m;
- Kirovsky district – 57,083 rubles/sq.m.;
- Leninsky district – 65,930 rubles/sq.m;
- Oktyabrsky district – 75,545 rubles/sq.m.;
- Pervomaisky district – 57,034 rubles/sq.m.;
- Sovetsky district – 83,934 rubles/sq.m;
- Central district – 88,219 rub./sq.m.
City districts
Novosibirsk is located on the right and left banks of the Ob. The right bank areas include:
- Zheleznodorozhny is the oldest district from which its history began;
- Central is the smallest and largest district of Novosibirsk; it is actually the city center;
- Zaeltsovsky is the largest district, on the territory of which there is untouched taiga at almost every step, which is why Zaeltsovka is called “the lungs of Novosibirsk”;
- Kalininsky is one of the youngest districts of the city, cozy, with developed infrastructure, but nearby is the NCCP, which produces nuclear fuel;
- Dzerzhinsky is an area of contrasts, where new residential areas are combined with the private sector;
- Oktyabrsky (borders on Dzerzhinsky) is one of the oldest districts, which was formerly called Zakamensky (Kamenka is a river separating the district from the city center);
- Pervomaisky is an area without borders, consisting of several workers’ settlements, the private sector and residential areas.
There are only two left-bank districts of Novosibirsk:
- Kirovsky - the main development of the industrial zone, among which are woven residential areas;
- Leninsky - was separated from Kirovsky, the most densely populated district of the city.
Separately, it is worth noting the Sovetsky district, which is located on both the right and left banks of the Ob. It is there that the famous Akademgorodok is located, a city within a city, whose residents consider themselves only partly Novosibirsk residents.
Botanical Garden
You can have a good time in the largest Botanical Garden in the Asian part of Russia. The Central Siberian Botanical Garden covers an area of 1000 hectares. Due to the geographical location of Novosibirsk, on the territory of the botanical garden you can see plants that are representatives of the tropical and subtropical climatic zones. Incredibly beautiful forest, mosses, lichens, rare plants - all this will allow you to forget about business and problems for a while and give you the opportunity to enjoy unity with nature.
Despite the geographical location of Novosibirsk and its distance from Moscow by almost 3000 km, this city in Russia is a must-see.
Sights of Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is a young city, but there is a lot to see. Theatergoers should visit the Globus Theater and the Opera and Ballet Theater. Their buildings are distinguished by their unique architecture.
An excellent place for a family holiday is the Novosibirsk Zoo.
If you plan to walk, you can visit the Embankment, numerous parks, squares and gardens of the city, the Chapel of St. Nicholas - a business card, a symbol of the city on Red Avenue.
Novosibirsk is the personification of modern Russia. Large industrial center. A city with a population of over a million, which is rapidly developing, turning into one of the pearls of Siberia. A city of contrasts, where ultra-modern business centers are combined with dilapidated barracks of the last century, industrial enterprises and residential areas with pristine forests. This is a great place for young families; here you can find decent work, suitable housing and all the necessary infrastructure.
Bus stations of Novosibirsk
In Novosibirsk, at the time of writing this article, there was one large bus station in the city center (Krasny Prospekt, 4), the main building of which was under reconstruction. Instead of the central bus station, there are small bus stations in different parts of the city, from where buses travel along a variety of suburban and intercity routes, as well as to some cities in the near abroad.
It is planned to open several bus stations on the outskirts of Novosibirsk soon, which can be reached by regular city buses and minibuses.