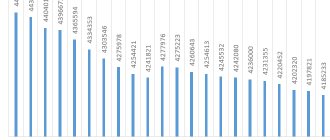
List of cities in the Rostov region by population
23 cities are part of the region, of which 7 cities have a population of more than 100 thousand people, 5 cities have a population of more than 50 thousand. The remaining settlements are home to between 15 and 50 thousand people:
- Rostov-on-Don.
- Taganrog.
- Salsk.
- Konstantinovsk.
- Millerovo.
- Bataysk.
- Mines.
- Volgodonsk.
- Belaya Kalitva.
- Aksai.
- Red Sulin.
- Novoshakhtinsk.
- Morozovsk.
- Tsimlyansk.
- Zernograd.
- Azov.
- Proletarsk
- Gukovo.
- Donetsk.
- Novocherkassk.
- Semikarakorsk
- Zverevo.
- Kamensk-Shakhtinsky.
Brief summary
From the above information we can conclude: the fewest inhabitants live in the Far East (population density - 1.2 people per sq. km) and in Eastern Siberia (population density - 2 people per sq. km).
The population density of the North is 1.03 people per square meter. km.
Population density of the North
In the European part of the Russian Federation, the highest population density is in the Moscow region, and the lowest density is registered in the Arkhangelsk region.
In the Asian part, the territory with the lowest density is Chukotka, and the highest population density is in the Sakhalin region.
Big cities
The list of cities in the Rostov region should start with large settlements. For example, the main administrative center is Rostov-on-Don. This is a metropolis in the south of Russia, home to more than 1 million people.
It was founded in 1749 by order of Elizaveta Petrovna on the banks of the Don River and not far from the Sea of Azov. Rostov-on-Don ranks 10th among megacities in terms of population. It is a large industrial, cultural, educational and administrative center.
Taganrog and Shakhty occupy the 2nd and 3rd positions in the region, respectively, where 253 and 237 thousand people live.
Taganrog is a historical city in Russia, which was founded by Peter I in 1698. It became the first port on the sea coast and remains so to this day. Mines is an educational and industrial city where coal is mined. A diocese is being created here, thanks to which it becomes a cultural and Orthodox center in the Eastern Donbass region.
The list of cities in the Rostov region, where the population exceeds 100 thousand, is completed by 4 cities: Volgodonsk, Novocherkassk, Bataysk and Novoshakhtinsk.
Volgodonsk is a young city. It was formed in 1950. Despite this, it is recognized as the energy center of the south, where the Atommash enterprise, engaged in the production of nuclear energy, was created.
Bataysk, founded in 1769, is a satellite town. Novocherkassk is the industrial center of the region and occupies a leading position in terms of production per capita. Novoshakhtinsk was once the place where the most coal was mined, but recently the mines have been closed. The food and light industries began to develop here.
Expert: “The process of extinction of the Rostov region is underway”
The population of the Rostov region is declining every year, although the government is spending more and more money on the largest national project “Demography”. At the end of 2022, 36.5 thousand people were born in the region, and 64.2 thousand died. The authorities believe that the situation was greatly influenced by the pandemic, but experts say that the decline in the birth rate and the increase in the number of deaths began in 2016. Participants in a round table in the regional Legislative Assembly discussed how the problem of demography can be solved, whether it is true that there are more pensioners in the region than children, and whether it makes sense to pay money for the birth of a child.
What are the results and what to expect?
As of January 1, 2022, approximately 4.2 million people live in the Rostov region. The main reason for the population decline is still natural decline; in 2022 alone it amounted to almost 28 thousand people.
As Igor Zhitnikov, Candidate of Economic Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Statistics, Econometrics and Risk Assessment at RINH, said, mortality rates in the Rostov region in 2022 could set a historical record: last year 64,277 people died in the region, which is an increase of 8,206 (or 14.7%) more than in 2022 (56,021).
— Based on the results of the first three months of 2022, 18.6 thousand people died in the region. If we extrapolate for a year, we get the number of deaths in the region of 74 thousand people. Our maximum mortality rate was in 2003 - 71.6 thousand. Of course, last year was greatly affected by the coronavirus, but in general this trend has been observed for the last ten years,” Zhitnikov said.
In 2022, the lowest birth rate was recorded - 36.5 thousand people. The closest value for this indicator was only in 1999 - then 33.4 thousand people were born. As Zhitnikov says, this is explained by the demographic hole of the late 1980s - early 1990s, that is, the younger generation, the smallest, is now entering reproductive age.
- There's nothing you can do about it. There are simply fewer of them physically. And I think that the number of births will decline and will reach its historical minimum by the end of the twenties,” says Zhitnikov.
In the Rostov region, according to him, a regressive age structure of the population has developed: there are more elderly people than children. In 2020, the share of pensioners in the entire population was 26.6%, the share of children under 16 years old was 17%.
- This is bad. Figures show that the process of extinction is underway in the Rostov region. And this also means that the working population of the region has an additional burden: on average, per thousand people there are 772 people before and after working age {in 2010 - 636 people - Donnews.ru},” the expert said.
The only bright spot is infant mortality. If in 1999 the overall ratio was just over 21 ppm, then in 2020 it is 5.4 ppm.
How to solve a problem?
Alina Lazun, head of the labor department of the Ministry of Labor and Social Development of the Rostov Region, believes that transferring mothers on maternity leave or those with children under 5 years old to remote work would help increase the birth rate.
“My colleagues and I came to the conclusion that parents do not want to have children because they are so busy. When you work from morning to evening, there is simply no one to leave your child with. Today, much attention is paid to remote work. The pandemic not only gave us problems, but also opened up new formats. If mothers could combine work and care for children, this would also give results,” Lazun suggested.
According to Legislative Assembly deputy Sergei Kosinov, an erroneous decision was made when payments for the first child began. He believes that this measure does not increase the birth rate, since they already pay less for the birth of a second child.
“We must understand that in order to change demographic processes, families with three children must appear in large numbers. At the same time, a large family should not be poor. Why not consider the possibility of paying the family a large sum from the budget, for example, 1.5 million rubles at the birth of the third and subsequent children,” Kosinov said.
He also proposed considering a “parental salary,” that is, paying one of the spouses an additional salary until the child reaches 18 years of age.
Rosstat has developed a forecast of life expectancy in the Rostov region until 2030. According to an optimistic forecast, the population of the region will remain at the level of 2022; according to a pessimistic forecast, it will decrease by 200 thousand people. But experts are confident that if specific measures are not taken and the situation with coronavirus is not reversed, these numbers will be much higher.
Paying money for the birth of a child is a road to nowhere
It is interesting that the state, and even the deputies, have a not entirely correct opinion about how to solve demographic problems: they say, if you give a family money, the birth rate will immediately increase. But money received for nothing makes you want to spend it rather than give birth. And such material incentives only lead to children being born to those who are not morally and socially prepared to raise them. And as a result, an increase in the number of children in orphanages and an increase in crime.
The world has long been stimulating fertility in other ways.
For example, in the UK they are implementing programs that help solve the main problems that young families face today: conflicts in the family amid a high number of divorces, teaching communication ethics; In Germany, the birth rate is increasing due to migrants. By the way, Russia was also advised to follow this path. Natalia Podolskaya
Population density of the Russian Federation by year
Table: population density of the Russian Federation by year
| Year | Population | Density (persons per sq. km) | Population growth (%) |
| 2000 | 146 662 563 | 8.57 | -0.33 |
| 2001 | 146 109 536 | 8.54 | -0.38 |
| 2002 | 145 506 821 | 8.51 | -0.41 |
| 2003 | 144 889 334 | 8.47 | -0.42 |
| 2004 | 144 313 531 | 8.44 | -0.40 |
| 2005 | 143 833 240 | 8.41 | -0.33 |
| 2006 | 143 480 487 | 8.39 | -0.25 |
| 2007 | 143 259 328 | 8.37 | -0.15 |
| 2008 | 143 151 706 | 8.37 | -0.08 |
| 2009 | 143 124 912 | 8.37 | -0.02 |
| 2010 | 143 142 380 | 8.37 | 0.01 |
| 2011 | 143 184 788 | 8.37 | 0.03 |
| 2012 | 143 249 506 | 8.37 | 0.05 |
| 2013 | 146 347 100 | 8.55 | 0.07 |
| 2014 | 146 666 900 | 8.41 | 0.22 |
| 2015 | 146 270 033 | 8.55 | 1.81 |
| 2016 | 146 330 004 | 8.60 | 0.04 |
| 2017 | 146 389 999 | 8.57 | 0.04 |
The population density during the existence of the Soviet Union was 8.61 people per square meter. km.
Coal mining
The Rostov region is undoubtedly one of the main coal mining regions. Although most of the mines in the region have closed recently, the Russian government still allocates part of the budget to restore and maintain the proper level of the main mining areas of the region.
Here is a list of cities in the Rostov region that currently mine such an energy-important resource as coal:
- Kamensk-Shakhtinsky;
- Shakhty;
- Belaya Kalitva;
- Donetsk;
- Gukovo;
- Novoshakhtinsk.
Social and demographic status
The Rostov region, according to Rosstat, is a promising region for the population. Therefore, in general, the demographic and migration situation in many cities of this subject is constantly growing. But not in all of them.
This list of cities in the Rostov region contains 5 settlements with the best indicators related to the quality of life of the population, healthcare, education and other socially significant parameters that affect the standard of living.
- G. Aksai. The city itself and the entire Aksai district rank first in the rankings of the best areas in many economic and social parameters. This is the best area in the region for promising development.
- City of Rostov-on-Don. It is not surprising that the capital of the region has the best indicators in terms of living standards and demographics. The city has the highest population growth, high average wages and the highest birth rate. Although, according to Rosstat, in the general ranking of districts of the Rostov-on-Don region it occupies only third position (after Aksaisky and Myasnikovsky districts), among urban settlements it ranks first.
- G. Taganrog. Although this small city is inferior in demographic and migration indicators to the center of the region, the level of access to education and employment for the population throughout the region is very high.
- G. Volgodonsk. Economically, this city is very important. It houses factories of various types, and the Volgodonsk Nuclear Power Plant is located on the Tsimlyansk Reservoir. All these production facilities provide many jobs and high wages. Therefore, both social indicators and the entire infrastructure in Volgodonsk are at the proper level.
- G. Azov. Located next to the Sea of Azov on the left bank of the Don River, it has a strategically important position and is constantly developing.