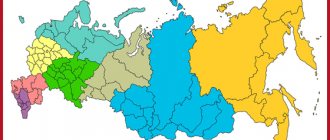
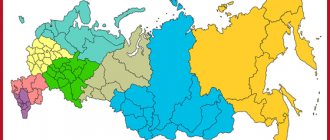
Our top 10 largest regions of Russia will tell you about the largest constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
The Murmansk region is located in the north-west of the European part of Russia and is part of the North-Western Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Murmansk.
Tourists in love with northern nature flock to this region. After all, here you can see the midnight sun, daytime stars and the mesmerizing northern lights. According to 2012 data, 787.6 thousand people live in the Murmansk region.
This region covers an area of 144.9 thousand square meters. km.
The Vologda region is located in the north of the European part of Russia and is part of the Northwestern Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Vologda.
This ancient Russian city contains a rich history around which tours around the region concentrate. According to 2005 data, 1245.5 thousand people live in the Vologda region.
This region covers an area of 145.7 thousand square meters. km.
The Novosibirsk region is located in the Asian part of Russia and is part of the Siberian Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Novosibirsk.
Tourists come to this region mainly for two reasons: skiing and unique nature. People are also attracted to healing springs and mud.
According to 2012 data, 2686.9 thousand people live in the Novosibirsk region. This region covers an area of 177.8 thousand square meters. km.
The border separating Europe and Asia runs through the Sverdlovsk region. The region is part of the Ural Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Yekaterinburg.
This area contains famous religious sites: the Orthodox Cathedral of the Exaltation of the Cross and the Buddhist monastery of Shad Tchup Ling. According to 2014 data, 4320.7 thousand people live in the Sverdlovsk region.
This region covers an area of 194.3 thousand square meters. km.
Tomsk region is located in the Asian part of Russia and is part of the Siberian Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Tomsk. In this area, known for its taiga-swamp nature, there is the Vasyugan swamp - the largest in the world. According to 2015 data, 1074.5 thousand people live in the Tomsk region. This region covers an area of 314.3 thousand square meters. km.
The Amur Region is located in the south of the Far East and is part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Blagoveshchensk. This area is famous for its unique Burning Mountains in the Szymanovsky region, which have been smoking for over 300 years. According to 2004 data, 894.5 thousand people live in the Amur region. This region covers an area of 363.7 thousand square meters. km.
The Magadan region is located in the east of the Asian part of Russia and is part of the Far Eastern Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Magadan.
One of the most picturesque places in the region is Jack London Lake, which is bordered by mountain ranges and coniferous forests. According to 2010 data, the Magadan region is home to 161.2 thousand people.
This region covers an area of 462.5 thousand square meters. km.
Arkhangelsk region, with a population of 1304.5 thousand people. (according to 2005 data) is located in the north of the European part of Russia and is part of the Northwestern Federal District.
The administrative center is the city of Arkhangelsk. The region includes the Nenets Autonomous Okrug.
Taking into account its territory, as well as the area of the sea islands, the area of the Arkhangelsk region is 587.4 thousand square meters. km.
The Irkutsk region is located in the Asian part of Russia and is part of the Siberian Federal District. The administrative center is the city of Irkutsk.
The center of tourism in the region is Lake Baikal, known for its clean and transparent water, which allows you to see the bottom at a depth of 40 m. According to 2007 data, 2513.8 thousand people live in the Irkutsk region.
This region, including the district, covers an area of 774.8 thousand square meters. km.
The Tyumen region is located in the west of the Asian part of Russia and is part of the Ural Federal District. Geographically, the region includes the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The administrative center of the region is the city of Tyumen. According to 2015 data, 1429.2 thousand people live in the Tyumen region. This region occupies 1464.2 thousand square meters. km.
Russia includes 83 regions that vary in size. Some of them occupy a larger territory than other European states (for example, France or Great Britain).
Source: https://top5-top10.ru/top-10-samyx-bolshix-regionov-rossii/
What holiday is it today?
09 February 2022, Wednesday
Today are holidays and events: Aeroflot's birthday International Dentist Day Memorable date in Russian military history: The feat of the cruiser Varyag Tomorrow: Diplomat's Day
Today is an Orthodox holiday: Transfer of the relics of St. John Chrysostom, Archbishop of Constantinople... Tomorrow: St. Ephraim the Syrian. Venerable Ephraim of Novotorzhsky. Venerable Ephraim of Pechersk, Bishop of Pereyaslavl. Venerable Theodosius of Totem, the head and founder of the Spasosumorin monastery...
Today is a national holiday: Chrysostom's Fire... Tomorrow: Ephraim's Day...
Seasons
Seasons, four periods of the year (spring, summer, autumn and winter) characterized by certain average temperatures. The period during which the Sun passes through one of these sectors is called the season. Spring in the Northern Hemisphere and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere begin when the Sun passes through the initial circle of declination and its right ascension is 0° (vernal equinox). Summer in the Northern Hemisphere and winter in the Southern Hemisphere occur when the sun's right ascension is 90° (summer solstice). Autumn in the Northern Hemisphere and spring in the Southern Hemisphere begin when the sun's right ascension is 180° (autumnal equinox). The beginning of winter in the Northern Hemisphere and summer in the Southern Hemisphere is considered to be the winter solstice, when the direct ascension of the Sun is 270°... Next: Seasons. Russian folk calendar. Monthly words...
Mushrooms of the Vladimir region
Of the edible mushrooms and mushrooms that are edible subject to special preparation measures, the following are found in the Vladimir region: saffron milk caps, boletus mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, porcini mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, chanterelles, russula, fly mushrooms, champignons, boletus mushrooms, and hill mushrooms.
The mushroom season begins in early spring, when the first morels and honey mushrooms grow. In summer, porcini mushrooms, russula, and fly mushrooms appear. From the end of summer, mushroom pickers' baskets begin to fill with boletuses and saffron milk caps.
Among the poisonous mushrooms common in this area are: pale toadstools, false mushrooms, and red fly agaric. The special danger of these mushrooms lies in the fact that in appearance they are doubles of edible mushrooms, so when going into the forest, it is important to know their distinctive features.
Folk calendar about every day
Every day one season always replaces another and this determines a person’s way of life. In connection with this, a folk calendar was formed in which there were practically no nameless, unmarked days. Every day was special, had its own purpose. All this was determined by climate conditions and astrological phenomena.
A calendar is a system for counting periods of time. The first calendars arose a long time ago, in ancient times, because there was a need to measure time. The word calendar comes from the Latin words caleo - to proclaim and calendarium - debt book. This is due to the fact that in Ancient Rome the beginning of each month was especially proclaimed, and because it was customary to pay debts on the first day of the month. Different peoples counted time differently. Some calendars are based on the changing phases of the moon - lunar calendars; in others - the change of seasons - sunny; in others, the length of the year was coordinated with the change of seasons, and the counting of months was associated with the phases of the Moon. Such calendars are called lunisolar.
In Rus', the calendar was called a monthly calendar. Every day, the month book covered the entire year of peasant life, “describing” day by day, month after month, where each day had its own holidays or weekdays, customs and superstitions, traditions and rituals, natural signs and phenomena. The cyclical nature of the calendar is reminiscent of human life, where spring is youth, summer is heyday, autumn is the time of harvesting fruits (it’s good if there are some, otherwise you can live your life without collecting fruits), winter is the time of wisdom and peace. This cyclicality and rhythm determined the way of life of the farmer. The folk calendar was an agricultural calendar, which was reflected in the names of the months, folk signs, rituals and customs. Even the determination of the timing and duration of the seasons is associated with real climatic conditions. Hence the discrepancy between the names of the months in different areas... Next: Folk calendar...
Fishing calendar for every day
The fishing calendar should not be taken as an absolutely indisputable truth. Fish biting is greatly influenced by a whole range of natural factors, as well as the influence on the nature of man himself. You must not forget that the fish’s bite depends and is determined not only by the calendar dates and biological cycles of their life, reflected in the calendar, but also, no less, by the state of their habitat; the bite also depends on weather conditions: air and water temperatures, cloudiness, wind direction and strength, etc... Next: Fishing calendar...
Transport connection
On the map of the Vladimir region with its districts you can see a well-developed network of railways and roads. They serve the flow of cargo and passengers in three directions of the Trans-Siberian Railway. Part of the region is part of the capital's railway ring.
The satellite map of the Vladimir region shows highways passing through the territory in the direction of:
- Yaroslavl;
- Ryazan;
- Nizhny Novgorod.
The main highways of the region: A108, P72 and P125. There are two branches of oil pipelines running through the region. Vladimir has its own international airport.
Orthodox calendar about every day
Orthodox calendar: Orthodox, Church and Christian holidays.
The church year is an alternation of weekdays and holidays. On weekdays, a person is called to work “by the sweat of his brow to earn his bread.” Holidays are given in order to feel liberation, to rise above the bustle and routine of the world, to feel involved in the highest of worlds, “where there are no illnesses, sorrows and sighs, but endless life.” Since ancient times, holiday cycles have been associated with the seasons. The pagans associated them with the worship of the forces of nature, the cult of which in the Old Testament was replaced by gratitude to the Creator for the universe. And although the connection between holidays and the seasons has not completely lost its power, since God is present in everything, in the plant and animal world, in human works, it nevertheless faded into the background, giving way to a spiritual foundation built on the Sacred Scriptures. The history of Orthodox holidays dates back to the times of the Old Testament. Each of the Orthodox holidays is dedicated to the remembrance of the most important events in the life of Jesus Christ and the Mother of God, as well as the memory of saints... Next: Orthodox calendar...
Lakes of the Vladimir region
There are more than 4 hundred lakes in the region, their total area is 5 thousand hectares. Most of the lakes are shallow, have no drainage, and are quickly overgrown with a layer of peat. The lakes of the region have a variety of shapes: oval, horseshoe-shaped, round. The shores are most often either sandy or marshy. The coastline has simple outlines. Some lakes located in groups are connected by underground drains. Lakes have different origins; there are floodplain, karst, alluvial, and glacial lakes.
The largest lake is Kshara, whose depth is more than 60 meters.
Russian folk calendar for every day
The word “sign” comes from the word “notice”, i.e. observe. As a result of observing what happens around a person every day, he accumulates life experience. This knowledge was passed down from generation to generation, carefully preserved and people trusted it as a sacred book. Many signs have come to us from the depths of centuries without losing their knowledge. Each of us is free to choose: to dismiss all this as an absurd superstition or to take a closer look at the signs and take the centuries-old experience of generations more seriously. Most of us, when taking exams, ask them to scold them, boasting about some kind of good fortune or luck, spit so as not to jinx them or knock on wood, take a detour if a black cat crossed the road, are afraid of the number 13 and much more. And who among us does not have lucky things, numbers? Who has never resorted to the help of fate at least once in their life, who has not believed in secrets? It’s as if everything connected with signs is hidden somewhere deep in our subconscious. Often we remember them mechanically, unconsciously, or just as a joke. But, undoubtedly, the signs contain a lot of accurate knowledge and practical wisdom of our ancestors. They cover all the characteristic, often difficult to perceive, natural phenomena. Signs have preserved a lot of what was in old folk holidays and customs; they help predict the weather, grow crops... Next: Folk signs...
Flora of the Vladimir region
For a long time, the vegetation of the Vladimir region has undergone serious changes. Nowadays, the vegetation is mixed, largely represented by forests. Among all the regions of the Central Federal District of Russia, the Vladimir region is one of the richest in forests.
Among the species growing in forests, the leading place belongs to conifers - they occupy slightly more than half of the region’s territory. A third of the forests are small-leaved, a tenth are zonal broad-leaved forests. The most common trees in forests are pine, birch, spruce, and aspen. The total forest area is more than one and a half million hectares.
The area is rich in vascular and bryophyte plants. Among them there are also those that are listed in the Red Book, for example: real slipper, fingerroot, Lezel's liparis, burnt orchis and others. There are also common medicinal plants, such as St. John's wort, mint and others.
Holiday calendar, dates and events of the year
All state and professional holidays in Russia, including significant World and International holidays, and other equally interesting holidays and events about every day.
The holiday has always kept pace with the history of mankind. Social time can be divided into three types: everyday life (weekdays), weekends and holidays. Everyday life is a series of practices repeated day after day and every day (work). Weekends are regular breaks from the rush of everyday life. It is believed that on weekends a person should restore his strength after working days. Day off, non-working day. A holiday is a day of celebration established in honor or in memory of someone or something. A day or series of days celebrated by the church in memory of a religious event or saint... Next: Calendar...
Soil diversity of the Vladimir region
The following types of soils are found in the region:
fertile dark-colored carbonate, found in the forests of Opole gray forest, found in the same area
turf alluvial, found near the banks of the largest rivers
soddy-podzolic, subdivided into medium loamy, sandy loam and sandy types and found in coniferous and mixed forests
podzolic-bog and bog species, found in the area of the Gorokhovets bogs and Meshchera
It should be noted that soils contain insufficient amounts of boron and sulfur.
Prayer book, Orthodox prayers for every day
Prayer is the most powerful means for healing all illnesses - both physical and mental. Prayers can be laudatory or grateful, petitionary and repentant. If we have offended God, sinned, we must ask Him for forgiveness, that is, repent. Such prayers are called repentant prayers. If everything is fine with us, if we and our loved ones are healthy and prosperous, if we have a place to live, something to wear, something to eat, we must glorify and thank God for this. Such prayers are called praise or thanksgiving. If some misfortune, illness, trouble or need happens, you need to ask God for help. Such prayers are called petitionary... Next: Orthodox prayers...
Zodiac, astrological, eastern calendar. Zodiac signs
In ancient times, to establish the calendar, priests used knowledge of the positions of all the planets. Before the reform of Peter 1, the New Year was celebrated on the Day of the Autumn Equinox. On this day, according to ancient legend, the most peaceful treaty was concluded between the Great Race (ancient Slavs) and the Great Dragon (ancient Chinese) and it was approximately 7518 years ago... For the ancient Slavs, the calendar month corresponded to the lunar cycle from new moon to new moon, taking into account such Thus, the relationship of the entire annual cycle with astronomical and natural phenomena. There was no coherent calendar system. The main natural phenomena are still considered to this day to be the days of the solar equinox and solstice - the Slavic holidays Maslenitsa, Kupala, Ovsen and Kolyada. But during the time of Peter 1, all ancient Slavic calendars were abolished and a new Western European calendar from the Nativity of Christ (Julian calendar) was introduced, while the beginning of the calendar was moved to January 1. The Julian calendar (old style) did not take leap days into account and accumulated one extra day every 128 years. After the October Revolution in 1918, the Gregorian calendar (new style) was introduced in Russia, according to which an amendment of 13 days was introduced. The calendar of the ancient Slavs was based on two planets: the Sun and the Moon. And now they don’t use anything at all. The calendar has become static. There is no such thing as the calendar, it turns out, resting on some planet. Nobody even knows about it. There are just some standard numbers, there are months and holidays. The calendar is based on the Sun and Moon. Why is this so? Because these two luminaries influence the Earth. The Earth revolves around the Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. And these two luminaries create the atmosphere on the planet. From here the calendar is built... Next: Astrological calendar...
January 14, 1929 abolition of the Vladimir province. Formation of the Ivanovo industrial region, which included most of the districts and cities of the former Vladimir province. The Vladimir region
was formed by the Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR on August 14, 1944 from the districts of the Ivanovo, Nizhny Novgorod and Moscow regions. “Decision of August 14, 1944 on the formation of the Vladimir region as part of the RSFSR. 1. Form the Vladimir region within the RSFSR with its center in the city of Vladimir. The Vladimir region includes: cities - Vladimir, Alexandrov, Vyazniki, Gus-Khrustalny, Kovrov, Kolchugino and districts - Alexandrovsky, Vladimirsky, Vyaznikovsky, Gorokhovetsky, with the exception of 4 village councils (Zolinsky, Ilyinogorsky, Myachkovsky and Starkovsky), Gus- Khrustalny, Kameshkovsky, Kirzhachsky, Kovrovsky, Kolchuginsky, Kurlovsky, Melenkovsky, Nebylovsky, Nikologorsky, Selivanovsky, Sobinsky, Struninsky, Sudogodsky, Suzdal and Yuryev-Polsky, separating them from the Ivanovo region; the city of Murom and the districts - Lyakhovsky, Muromsky, with the exception of 7 village councils (Volosovsky, Efanovsky, Malyshevsky, Monakovsky, Okulovsky, Pozdnyakovsky, Spaso-Sedchinsky) and Fominsky, separating them from the Gorky region; Petushinsky district, mountains. Pokrov and 5 village councils (Glubokovsky, Ivanovsky, Kirzhachsky, Markovsky, Pernovsky and Slobodsky), Orekhovo-Zuevsky district, separating them from the Moscow region. 2. Include Zolinsky, Ilyinogorsky, Myachkovsky and Starkovsky village councils of the Gorokhovetsky district of the Ivanovo region into the Gorky region. 3. Approve: a) first secretary of the Vladimir regional committee of the CPSU (b) Comrade G.N. Paltsev, releasing him from the work of first secretary of the Ivanovo regional committee of the CPSU (b); b) the chairman of the executive committee of the Vladimir Regional Council of Workers' Deputies, Comrade V.V. Syrovatchenko, releasing him from the work of the chairman of the executive committee of the Vladimir City Council of Workers' Deputies; c) the first secretary of the Ivanovo regional committee of the CPSU (b) Comrade G.M. Kapranov, the current second secretary of the same regional committee of the CPSU (b).” “TO THE SECRETARY OF THE Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party (Bolsheviks) comrade. TO MALENKOV We are sending a draft resolution of the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks on the formation of the Vladimir region as part of the RSFSR, through the disaggregation of the Ivanovo region and the inclusion of the mountains in the Vladimir region. Murom, Lyakhovsky, Muromsky and Fominsky districts of the Gorky region, as well as one district completely and one partially of the Moscow region, which were previously part of the former Vladimir province. The issue of the formation of the Vladimir region and the inclusion of the districts of the Ivanovo and Moscow regions into its composition was agreed upon with the secretary of the Ivanovo regional committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks, Comrade Paltsev, and the secretary of the Moscow regional committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks, Comrade Chernousov. Secretary of the Gorky Regional Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks, Comrade Rodionov, objects to the inclusion of the city of Murom and three rural districts of the Gorky region into the Vladimir region. Comrade Rodionov motivates his objections by the fact that Mt. Murom and rural areas gravitate towards the mountains. Gorky, and Murom enterprises give their products to Gorky enterprises. These areas were transferred to the Gorky region only in January 1929, with the formation of the Ivanovo Industrial Region and the Nizhny Novgorod Territory, and not from the beginning of the revolution, as comrade reported in his telegram. Rodionov." The newly created region included 23 districts, 7 cities of regional significance, 10 cities of district subordination, 454 village councils. The total territory was 26.8 thousand square kilometers. The population size at the time of the creation of the region has not been established from archive documents, but it is known that two years later in 1946, 1 million 290 thousand 38 people lived in the region. The report of the first secretary of the Vladimir regional committee of the CPSU (b) Georgy Nikolaevich Paltsev indicated the restoration of historical tradition among the main reasons for the formation of the Vladimir region. The Vladimir region borders on the Moscow, Yaroslavl, Ivanovo, Ryazan, and Nizhny Novgorod regions. It is located 190 km from Moscow, the Vladimir lands extend in the north-eastern and eastern directions from the capital. The area of the Vladimir region is 29.1 thousand square meters. km, its population is 1449 thousand people (2008). The main rivers flowing through the region - Oka and Klyazma (with tributaries Kirzhach, Peksha, Nerl, etc.) - belong to the river basin. Volga. Navigation is carried out along the Oka and Klyazma (in the lower reaches). The Klyazma River (rivers of the Vladimir region) divides the region into almost two equal parts: northwestern and southeastern. In the northwestern part, on the plain (between the Koloksha and Nerl rivers), in its eastern sector, there is the famous Vladimir opole (height up to 236 m) - an almost treeless area with very fertile soils, the ancient granary of the Vladimir land. Vladimir opole is a unique black soil plot of land measuring 210 square meters. km – 30 × 7 km, formed as a result of burning of impenetrable forests by Slavic tribes. In general, we can say that in the north of the region the Moscow Upland passes into the flat Vladimir Opolye, and in the south the less developed Meshchera Lowland (Meshchera) extends. In the Vladimir region, mixed forests predominate, where mainly pine, birch, aspen, and spruce trees grow. Especially in the Meshcherskaya Lowland, quite large forests have been preserved; in the past they were called deaf and dense. It is not surprising that in this southeastern, partially swampy part of the region, there is only one ancient city - Murom (Melenki and Sudogda acquired city status in the 18th century, Gus Khrustalny - in the 20th century). The region is dominated by soddy, slightly podzolic soils, as well as gray forest and swamp soils. The Vladimir region has the most fertile soils; they served as the basis for the economy of the Vladimir-Suzdal principality, and have long determined the densest settlement of this particular part of the Vladimir land; here are the ancient cities of Suzdal, Vladimir, Yuriev Polsky. To the west, on the later developed plain, between the Kirzhach and Koloksha rivers, most of the Vladimir noble estates used to be located; there are no cities with a long history here, except for Alexandrov (Pokrov and Kirzhach became cities in the second half of the 18th century from the settlements near Monostyr). The Vladimir region is poor in mineral resources; there are only peat deposits. On the most significant scale, peat extraction is carried out near the town of Gus Khrustalny (see the village of Mezinovsky). The Vladimir region - a hilly plain - has a picturesque nature. The open spaces of fields, the smooth surface of river waters, the longitudinal bends of small rivers, oak groves with their age-old noise, preserved coniferous forests, flowering flax making the fields blue, pink fields of fragrant clover, touching blue cornflowers and other wildflowers and, of course, waves of golden ears on the fields (but there remains the sad realization that the area under grain crops is shrinking). The elevated terrain in the vicinity of the cities of Kirzhach - Kolchugino (236 m) has a special visual uniqueness. Among the state protected natural areas, the following sanctuaries stand out: Klyazminsky (formed in 1978, 21 thousand hectares, extends into the Ivanovo region) and Muromsky (1968, 56.2 thousand hectares), as well as the Meshchera National Park ( 1992, 118.9 thousand hectares). Four kilometers from the city of Alexandrov, the natural landscape complex of the German Mountains was created and protected. In pre-revolutionary Russia, the Vladimir province occupied one of the first places among industrial provinces. And after 1917, large enterprises were built on the former territory of the province, and industry actively developed. The patriotic rise of the population during the war years greatly contributed to the development of industry, which led to a significant increase in output. Compared to pre-war 1940, production volume was 162.7%. On the territory of the newly created region in 1944, the main industries were mechanical engineering, textiles, glass, and fuel extraction. The number of enterprises of union-republican significance was 530. The number of local enterprises was 4,783, with a total number of workers of about 200 thousand. The main enterprises of the region were those that are familiar to residents of the region under the names: Vladimir Tractor Plant, Vladimir Chemical Plant, Avtopribor, Vladimir Grammar Plant (future Tochmash), Kovrov Plant named after. Degtyarev, Murom Switch Factory, Gusev Glass Factory named after. E. F. Dzerzhinsky, Aleksandrovsky Radio Plant, Karabanovsky Cotton Mill named after. III International, Struninsky spinning-2 weaving and finishing plant “5th October” and many others. Along with weapons and ammunition, military and engineering enterprises produced river vessels, boats, radio stations, radio equipment, machine tools, measuring instruments for cars, and tractors. Glass factories supplied special products to the army and navy, window glass, and grade glassware. With such development of the territory for more effective management, the need arose to change the administrative-territorial subordination. To help the newly formed region, the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR decided to organize telephone and telegraph communication between Moscow and Vladimir, allocate housing for employees of the regional executive committee, cars and building materials, and equip a hotel and hostels. It was proposed to attract 400 unemployed citizens and 100 graduates of vocational schools and FZO schools as labor reserves. The plan also included the construction of an administrative building to house regional organizations. At the first meeting of the bureau of the Vladimir Regional Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks, held on September 9, 1944, priority tasks were set: placement of regional organizations, selection and approval of personnel, formation of a regional newspaper. Regional organizations are located in a building on the street. B. Moskovskaya, 58, which previously housed regional and city organizations (currently this is the building of the cultural and educational Vladimir-Suzdal Museum-Reserve). “COUNCIL OF PEOPLE'S COMMISSARS OF THE USSR DECREE No. 17832 rs dated September 2, 1944 Moscow, Kremlin. To locate regional organizations and institutions in the city of Vladimir, it is obligatory to: 1. The People's Commissariat of Health of the USSR (comrade Miterev), the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions (comrade Nikolaev) and the Main Sanitary Administration of the Red Army (comrade Smirnov) to relocate from the cities. Vladimir hospitals No. 5799, 1887 and from the village of Penkino hospital No. 4156, transferring the premises vacated by the hospitals to the disposal of the Vladimir Regional Executive Committee. Hospital relocation points will be established by the People's Commissariat of Health of the USSR and the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions together with the Main Military Sanitary Directorate of the Red Army. 2. Chief of Logistics of the Red Army Comrade. Khrulev and the Main Political Directorate of the Red Army (Comrade Shikin) to transfer the building occupied by the House of the Red Army to the city. Vladimir, to the balance of the regional executive committee for the placement of the regional committee of the CPSU (b). The House of the Red Army should be transferred to a building on III Internationala Street No. 33-35, transferring this building from the balance of the City Executive Committee to the balance of NGOs of the USSR. The Chief of Logistics of the Red Army must carry out the necessary repairs to the premises under the DKA. Remove the Raiprofsozh club of the Vladimir railway from the building being transferred to the House of the Red Army. node, city and district libraries immediately, and girls' secondary school No. 3 - in July 1945. 3. NGOs of the USSR (comrades Vorobyov and Khrulev) withdraw from the mountains. Vladimir to other points 105 road battalion, training and demonstration forge and the headquarters of the sapper brigade, transferring the vacated premises to the Vladimir Regional Executive Committee. 4. Allow the Vladimir Regional Executive Committee to use the premises currently occupied by the club to house its departments. Deputy Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR V. Molotov." “DECISION of the Executive Committee of the Vladimir Regional Council of Workers' Deputies of September 7, 1944. “On the placement of Regional organizations and departments of the Regional Council.” 1. To accommodate regional organizations and departments of the Regional Council, occupy the building of the House of Soviets, st. them. III International, house No. 58. 2. Oblige all heads of district, city and economic organizations by September 9 this year. d. vacate the space they occupy in the House of Soviets by moving to the premises indicated in the city council's relocation plan. 3. Assign to the executive committee of the City Council the left wing of the 2nd floor of the Council building. 4. Oblige the director of the Chemical Technical School, comrade. FROLOV and the head of Construction Department No. 5, T. PODGORNOV, within 24 hours, vacate the premises they occupy at houses No. 51 and 59 on the street. III International, owned by the City Council. 5. Propose to the executive committee of the City Council to use the vacant premises in houses No. 51 and 59 to house city organizations. 6. Oblige the executive committee of the City Council to take control of the implementation of this decision. Administrative eviction will be applied to organizations that have not complied with the decision by the specified deadline.” Particular attention was paid to the creation of a regional newspaper. The city newspaper “Prazyv” received the status of a 2-page regional newspaper. In 1945, 1 regional, 22 district, 22 large-circulation newspapers were published in the region with a total circulation of 108,792 copies. The plans of the regional committee of the CPSU (b) for 1946 were to increase the circulation of the regional newspaper to 30,000 copies and publish it on 4 pages. In 1944, a master plan for the development of the city of Vladimir was developed, thanks to which the center of a young, developing industrial region was created from a regional city. One of the most important tasks was the transformation of Vladimir into a cultural regional center. It is no coincidence that among the first decisions of the Vladimir Regional Executive Committee was the organization of a concert and variety bureau under the arts department of the regional executive committee, to which the building of the former Pyatnitskaya Church, used for warehouses, was transferred. It was decided to rebuild it as a philharmonic society and organize a concert hall in it. The artists of the concert and variety bureau gave concerts in military units, evacuation hospitals, kindergartens and schools. A plan for the improvement of the city's central square was developed. The territory on which the buildings of the Dmitrievsky and Assumption Cathedrals, the regional executive committee, the House of Officers, Pushkin Park and Lipki Park were located was to become one of the most beautiful squares in the cities of the Soviet Union.
House of Officers, Vladimir. Photo con. 1940s
In the pre-war and first war years, Vladimir fell into decay, and state control over the sights weakened. This is evidenced by the following incident: behind Kozlov Val there was a three-hundred-year-old cherry orchard, which before the revolution was called “Patriarchal”, in which all varieties of Vladimir cherries were represented. The City Council decided to give this garden to the meat processing plant and distillery for restoration. The managers of these enterprises decided to cut down the remaining cherry trees and planted cabbage there. They collected the cabbage and left the stalks, which were guarded by a watchman and did not allow volunteers to arrange the garden. In 1944, it was decided to restore the garden. But active work began only in 1948 after the first all-Union gathering of young gardeners, at which it was decided to create a “Garden named after 16 Union Republics”, the task of which was the preservation and restoration of horticultural crops. Currently, the garden has been returned to its historical name “Patriarchal”. It is working to revive varieties of Vladimir cherries.
Laying the garden of the Union republics. 1948
Garden named after the Sixteen Union Republics. Photo from the 1950s.
In 1944, collective and individual 5 gardening received special development. In the region, 159,404 workers and employees had vegetable gardens. In Vladimir, Kovrov, and Kolchugino, on average, about 140 kilograms of vegetables and potatoes were produced per year for each resident. Organizations provided assistance to gardeners with seeds and equipment. The development of household plots of the population was a serious food supply and played a positive role in improving the nutrition of residents of the Vladimir region. Prices at the central market of Vladimir, which in the 1940s was located in the city center in the area of modern 2nd Nikolskaya and Devicheskaya streets, gradually decreased. Thus, prices for meat, milk, flour, potatoes, and eggs decreased threefold in January 1945 compared to 1943; in regional cities the decrease was even more significant.
Central market of Vladimir.
Photo from 1947. The plans of the leaders of the Vladimir region included not only making 6 Vladimir a major center of mechanical engineering, but also preserving the glory of the ancient city. An interesting project was the construction of hydroelectric dams, which would turn the Klyazma into a high-water and navigable river, and build a riverine area in Vladimir. Attention was paid to the improvement of the cities of the region: Murom with its regular layout, ancient churches and monastery complexes, Kovrov with its chaotic, unplanned development. It was planned to transform Suzdal into a city-reserve of Russian antiquity. Thanks to the work to preserve historical monuments and picturesque architectural landscapes in the 1970s, the cities of the Vladimir region: Vladimir, Alexandrov, Murom, Suzdal and Yuryev-Polsky became part of one of the most popular excursion routes in Russia, the Golden Ring. The formation of the Vladimir region became an incentive for the development of the region. The growth of industrial enterprises and the national economy served the development of social and cultural infrastructure: in the period from the mid-1940s to the end of the 1980s, trolleybus lines were laid in Vladimir and Kovrov, buildings of city and district administrations, houses of culture were built throughout the region, dramatic theater, philharmonic, building of the regional library named after. Gorky and others. For the successes achieved in cultural and economic construction, development of industrial production, the Vladimir region and its cities: received high government awards: Vladimir region - Order of Lenin (1967), Vladimir - Order of the Red Banner of Labor (1971. ), passing Red Banners (1975, 1976), Kovrov - Order of the Red Banner of Labor (1978). ON THE. Yasashnova, employee of the State Archives of the Vladimir Region Articles about the city of Vladimir and the Vladimir region Natives and figures of the Vladimir province Vladimir province. 75th anniversary of the Vladimir region
Dream books online, interpretation of dreams
A dream book is nothing more than an interpreter of dreams and dreams, a translator of dreams. Since ancient times, people have been using dream books; dreams have always been given great importance, and people have often noticed the prophetic properties of some dreams. The dream book can become your faithful assistant every day and throughout your life, thanks to the dream interpreter you can always make the right decisions, the dream book will help you resist temptations in time, and will warn you against wrong steps and frivolous actions. Further…